Your Guide to Small Business Financial Management in 2026
To stay profitable in the small business landscape, you must track cash flow, control expenses, and make data-driven financial decisions. With that in mind, let’s explore key procedures for small business financial management, ways to simplify the process, and practical tips.
How to develop SOPs for small business financial management
For structured and organized financial management in small business, you need standard operating procedures (SOPs) – documented, step-by-step instructions that guide routine tasks. The basic ones include:
✅ Accounts receivable
✅ Accounts payable
✅ Tax compliance
✅ Budgeting and forecasting
✅ Financial reporting and audit
✅ Bank reconciliation
✅ Internal control
To implement these SOPs effectively, it is beneficial to rely on accounting software such as QuickBooks or Xero. They enable you to optimize invoice creation and tax filing, ensure accurate records, gain real-time insights, and automate and standardize financial workflows.
1. Accounts receivable
To ensure timely payment collection and reduce the risk of bad debt, develop a clear standard operating procedure for managing accounts receivable – the money owed for goods or services provided on credit.
A standard operating procedure for accounts receivable includes:
- Payment processing – define how invoices are generated, when they are sent, how payments are received, and how transactions are recorded. Indicate timelines for invoicing and updating customer accounts.
- Debt management – outline the steps for identifying and handling overdue accounts. Specify schedules for reminders, late fee conditions, non-payment escalation paths, and criteria for involving collections or legal counsel.
- Customer communication – provide straightforward instructions for contacting customers about outstanding balances. Include templates for payment reminders, dispute resolution procedures, and escalation steps for unresolved issues.
- Reporting and analysis – describe how to generate and review key reports such as aging schedules and cash flow projections. Lay out processes for reconciling data and identifying payment trends or collection challenges.
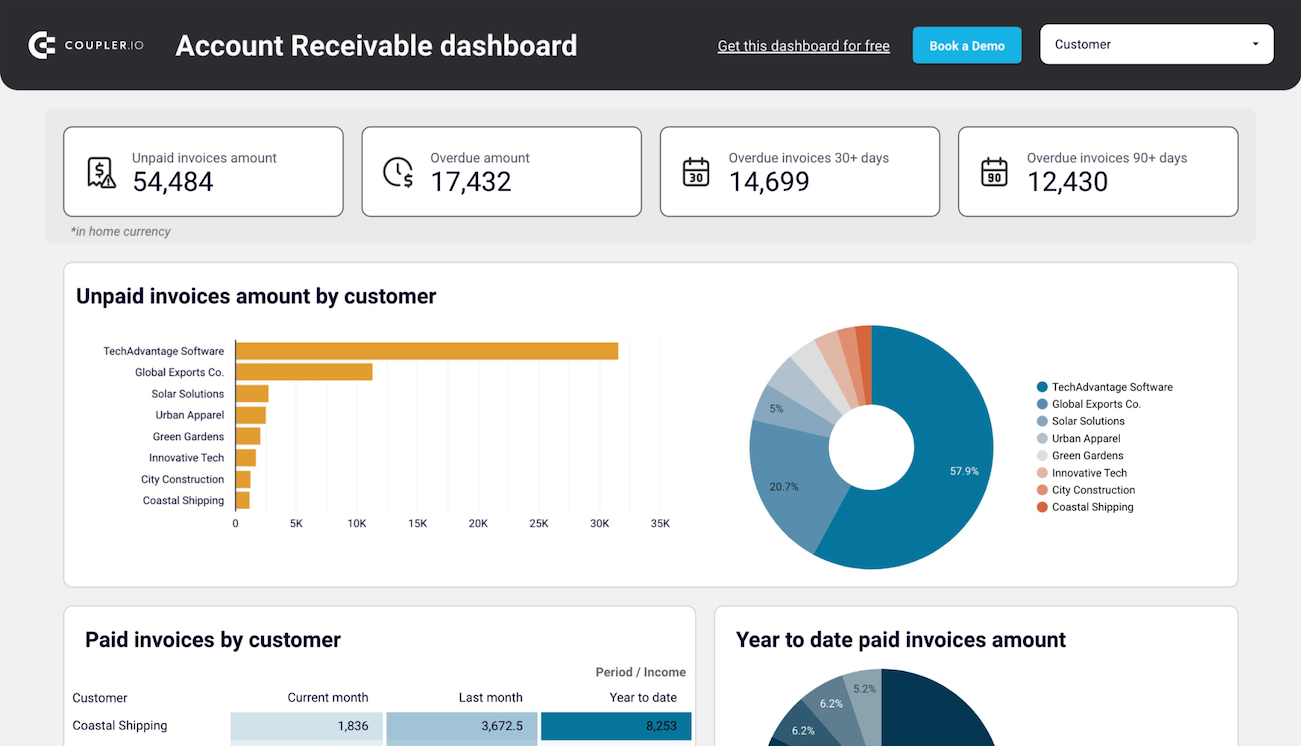
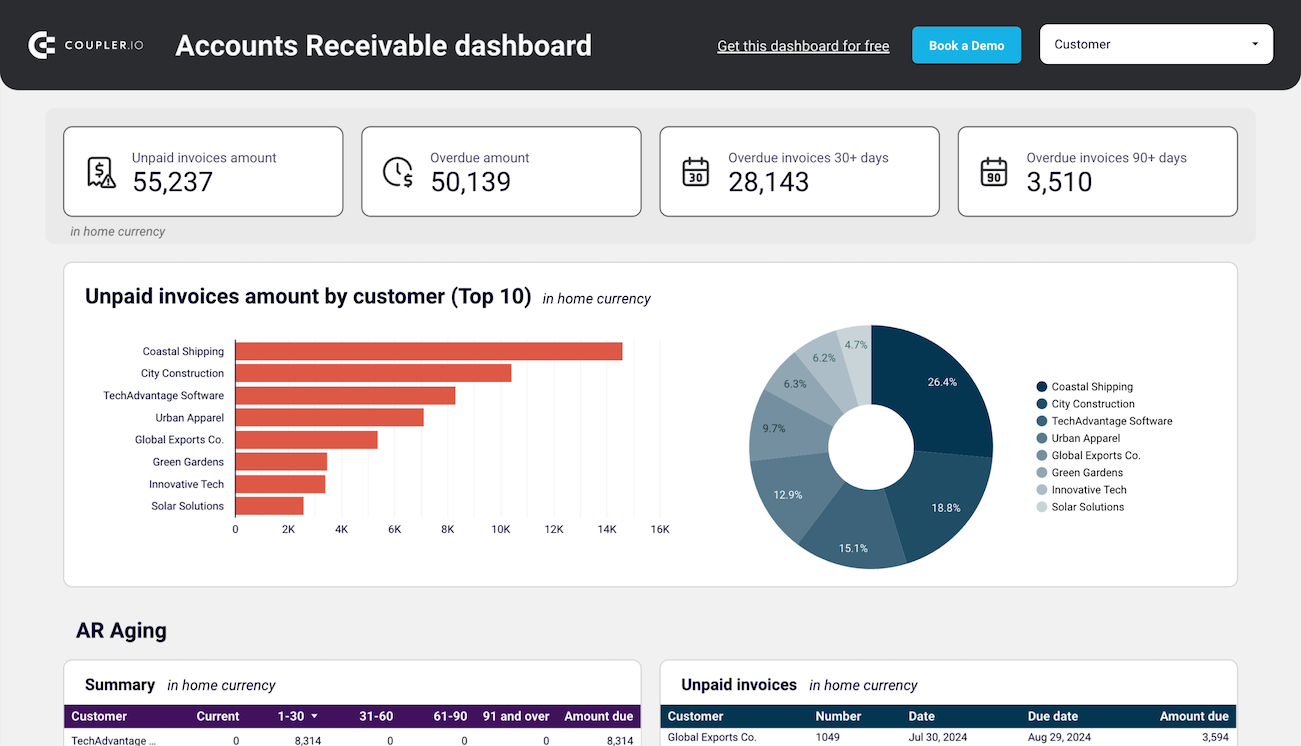
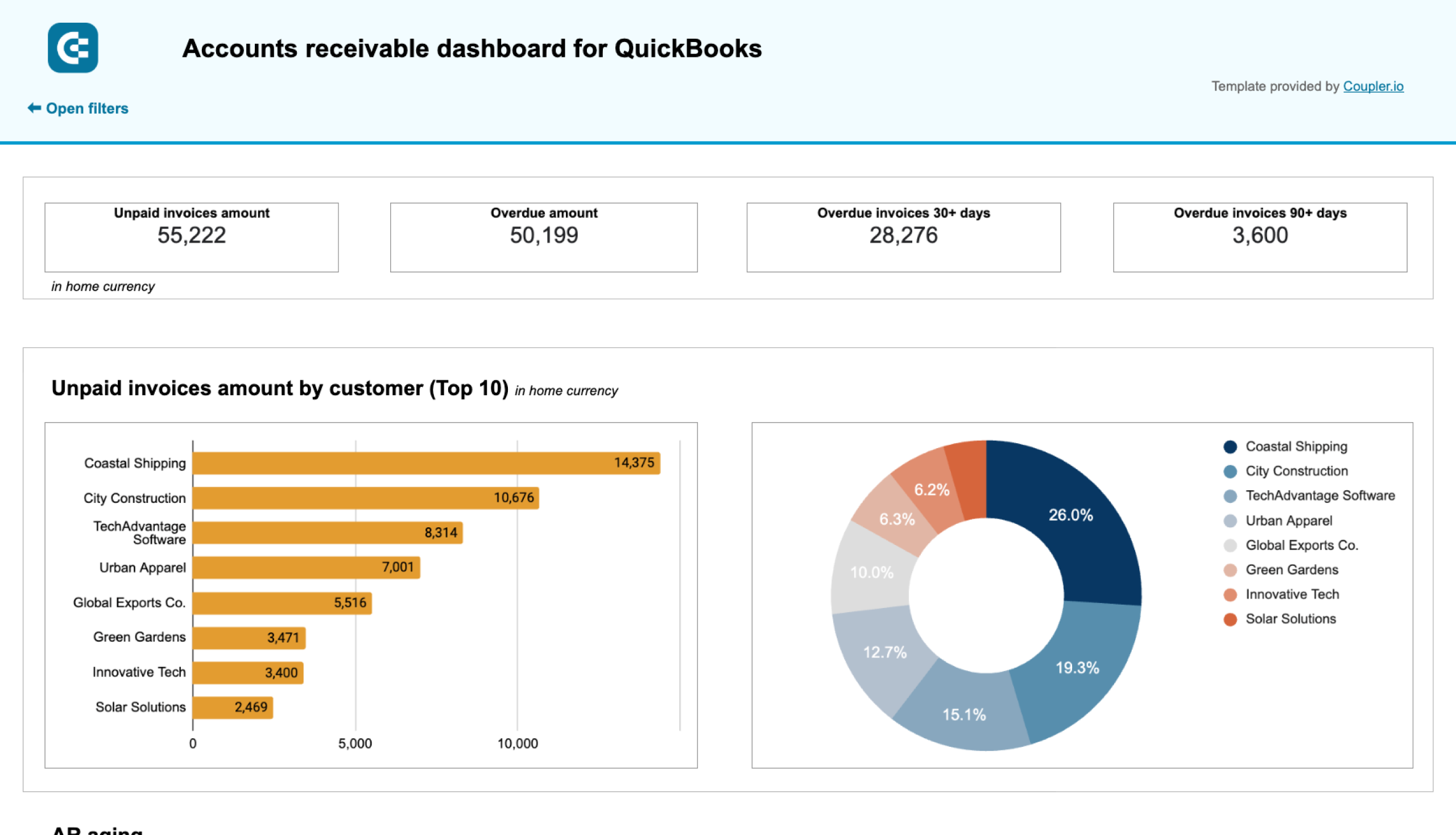
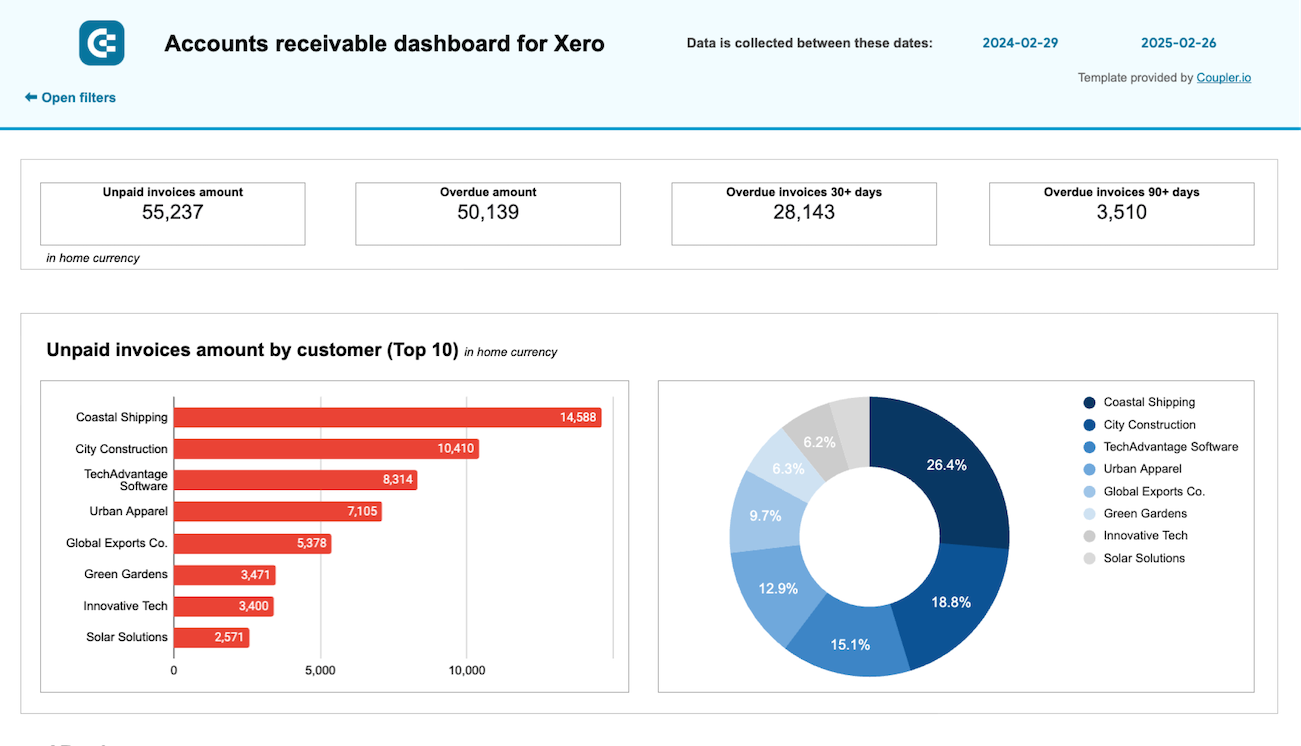
To identify your primary customers (debtors) and determine the amount they owe you, use report templates such as the accounts receivable dashboard by Coupler.io. It enables you to make informed decisions about communication with customers and activities to settle debts and prevent cash shortages.
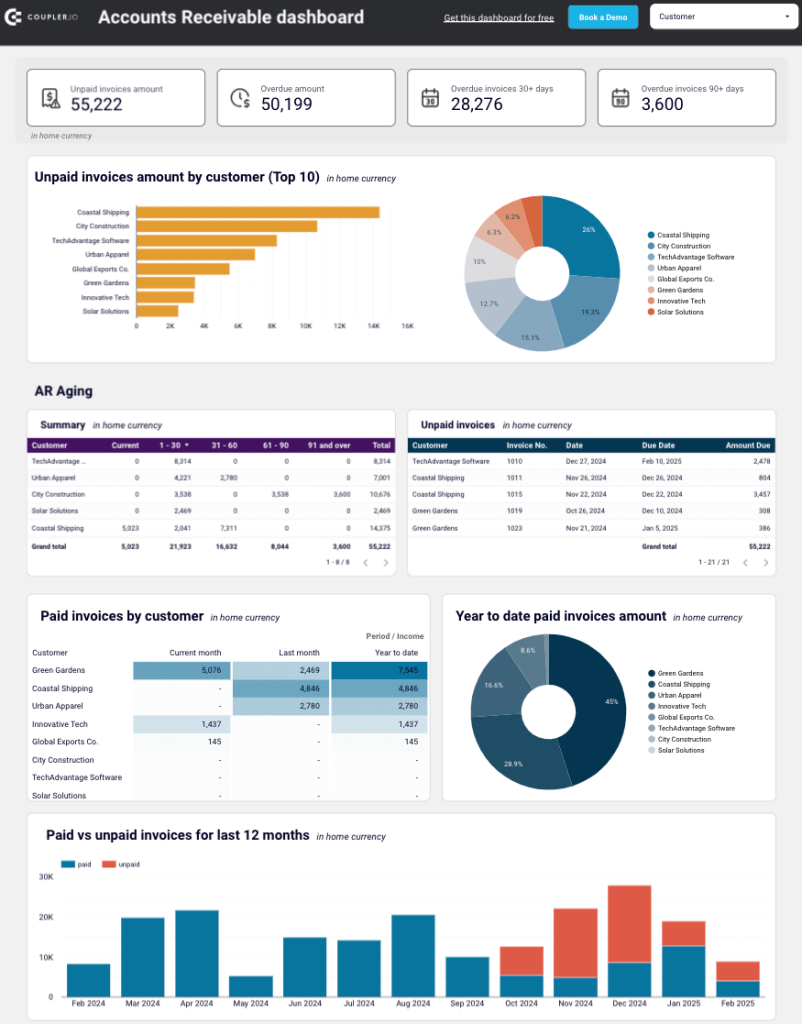
You can set up this financial performance analysis dashboard for both QuickBooks and Xero in Looker Studio and Google Sheets. To get started, follow the instructions in the template’s Readme tab to visualize your data.
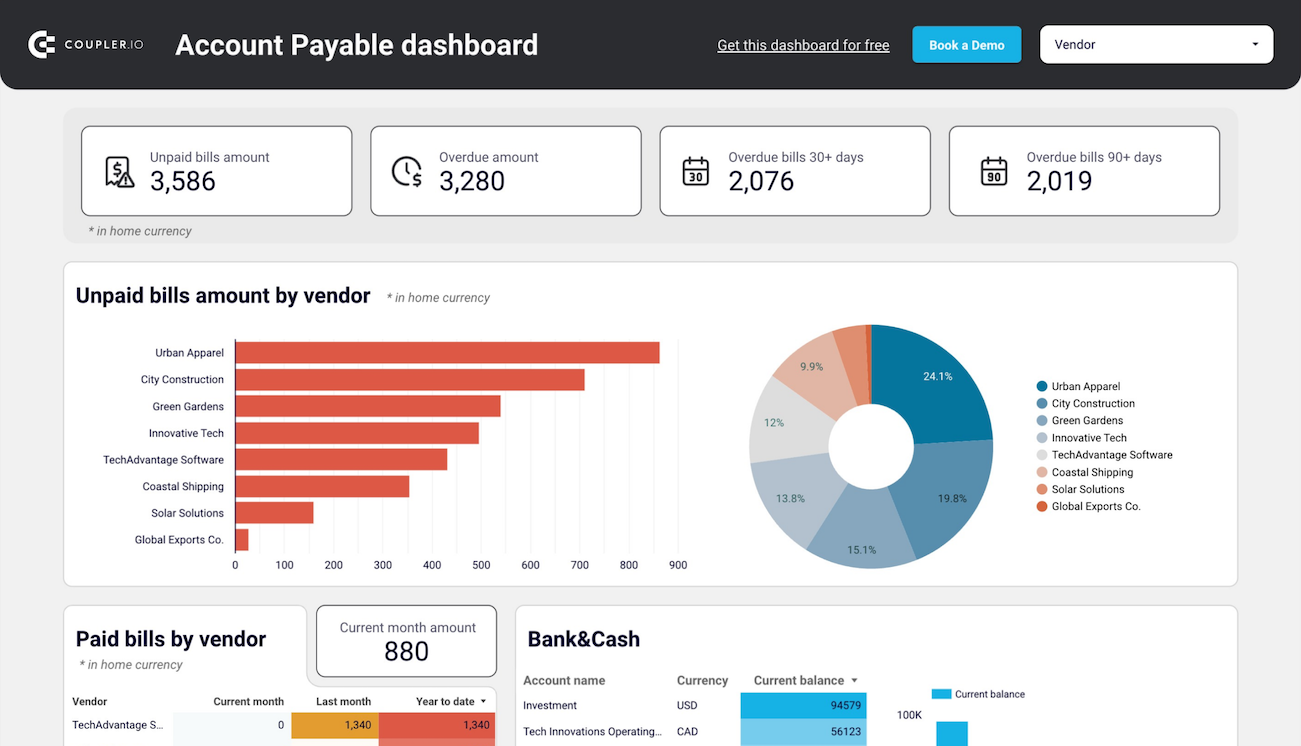
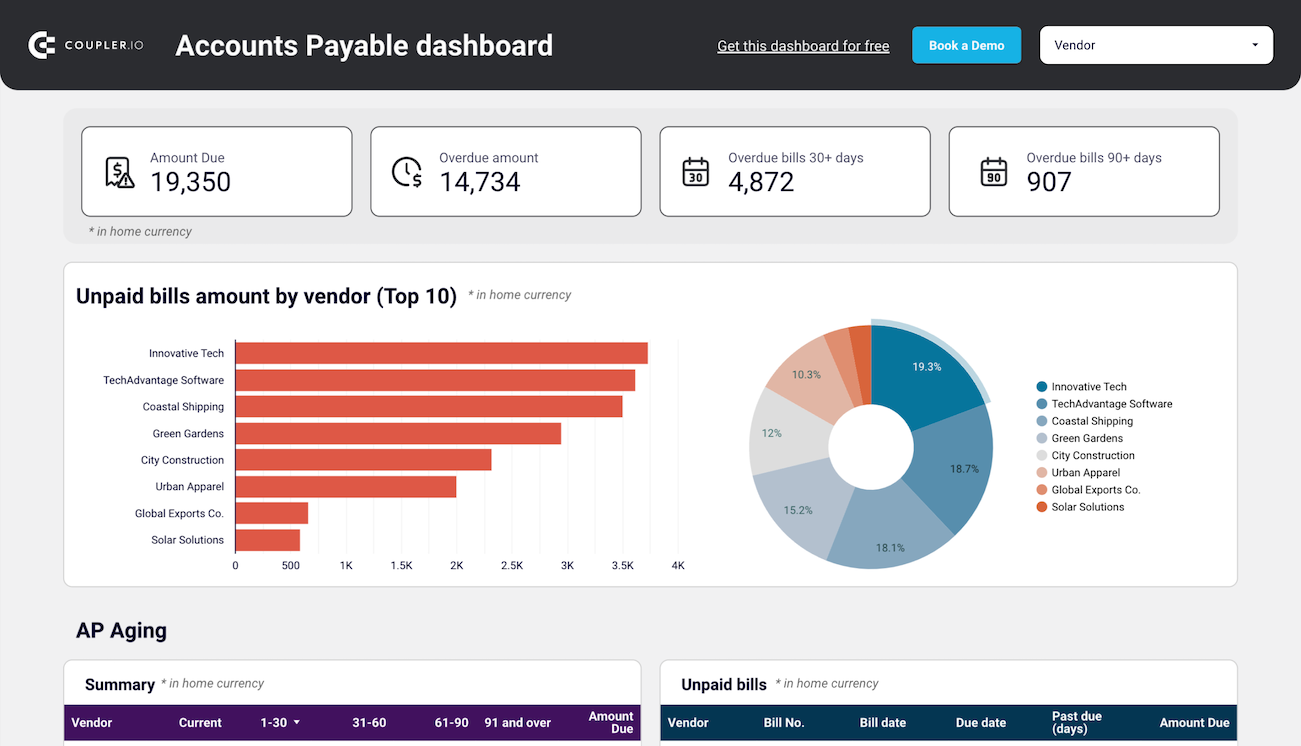
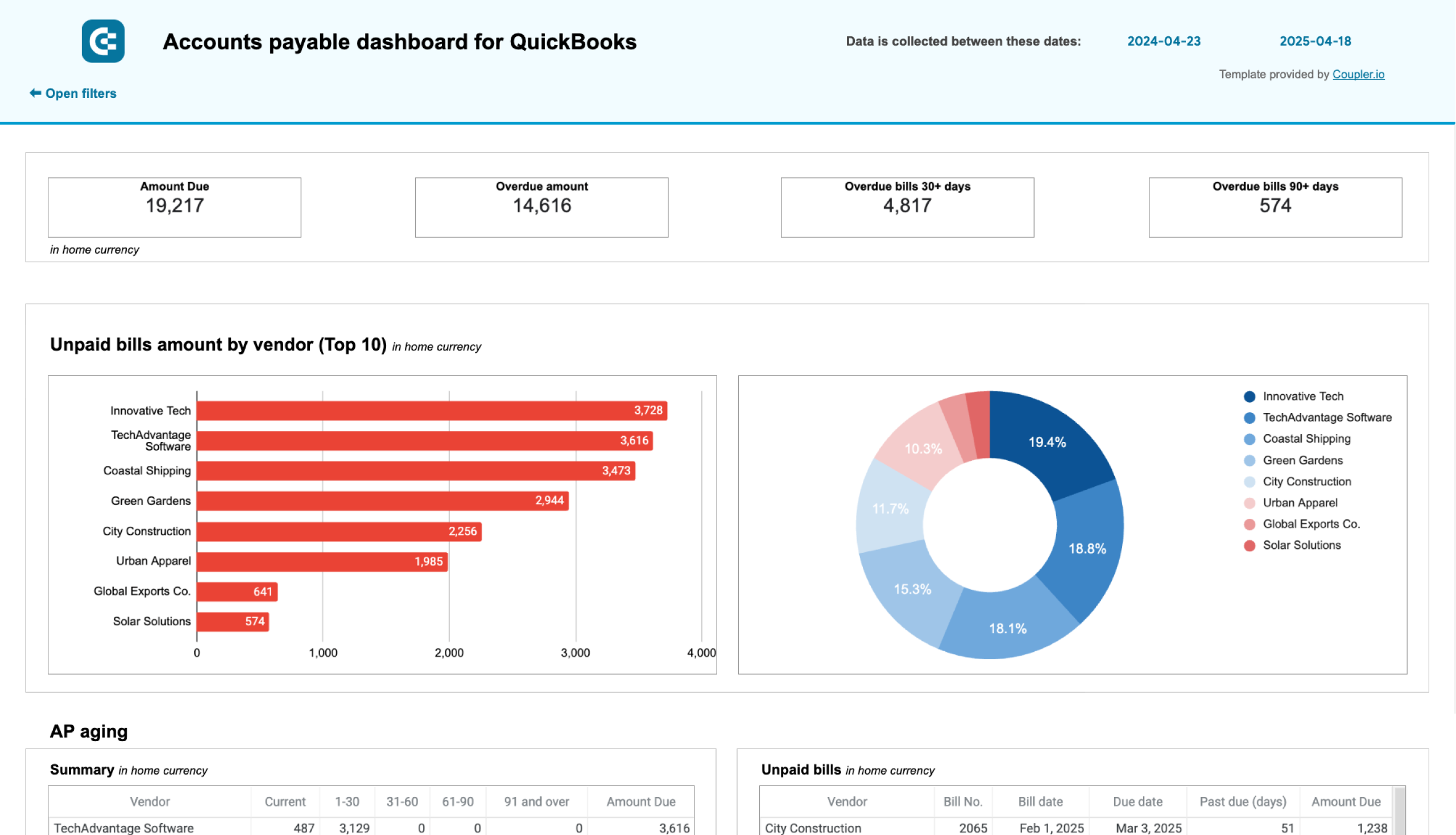
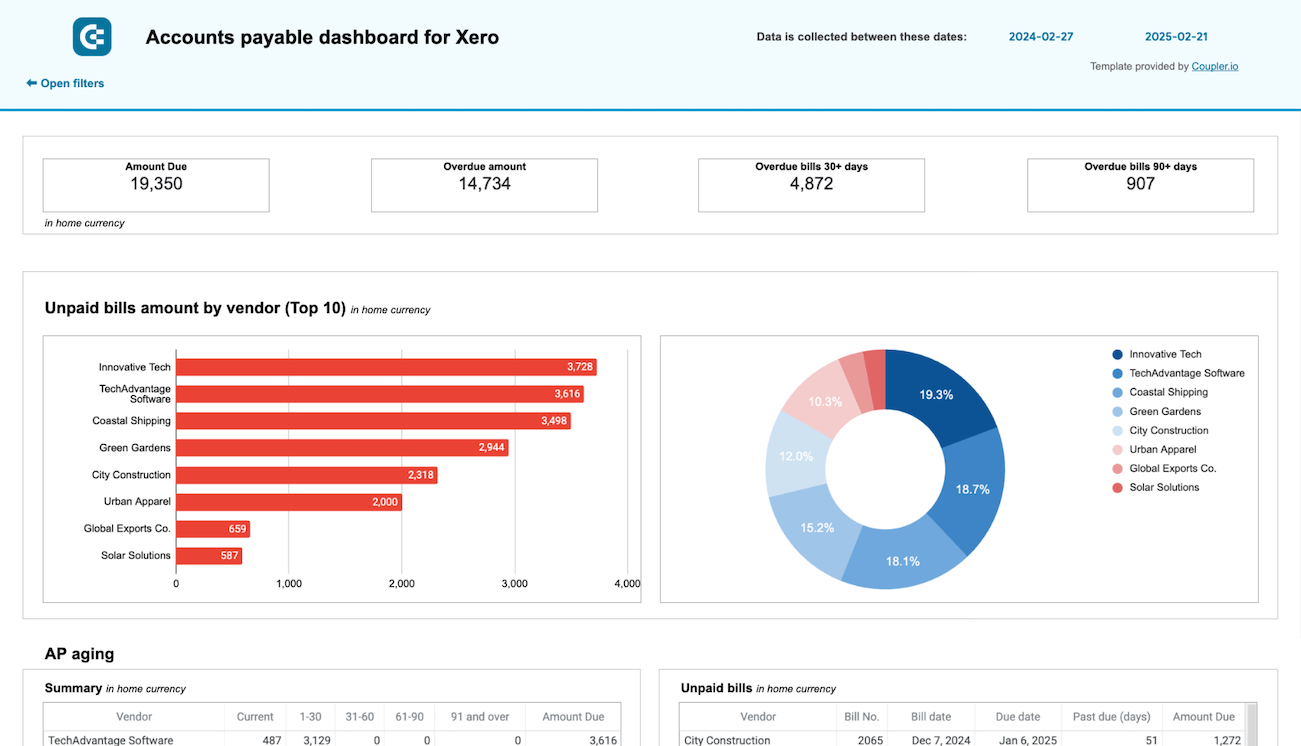
2. Accounts payable
In addition to managing incoming payments, it is essential to oversee outgoing obligations, avoid late fees, and maintain strong vendor relationships. To do this, an SOP for accounts payable is necessary – it addresses the amounts owed to suppliers for goods and services received.
This procedure consists of the following components:
- Invoice processing – define how vendor invoices are received, reviewed, and entered into the system. Include steps to confirm that goods or services were delivered as billed, check for discrepancies, and resolve any issues before approval.
- Approval workflow – outline the internal process for invoice approval, specifying who is responsible at each level and under what conditions. Indicate approval thresholds and escalation procedures.
- Payment terms and conditions – state the standard payment terms that the business follows. These could be net payment periods, early payment discounts, or late payment penalties. Ensure consistency with vendor contracts and cash flow policies.
- Processing of payments – describe the procedures for issuing payments, including method, required approvals, and documentation. Lay out steps for scheduling payments and managing exceptions or urgent disbursements.
- Vendor management – provide instructions for onboarding vendors, updating vendor information, and maintaining communication. Include steps to resolve disputes, verify contact and payment details, and review vendor performance periodically.
For insights into your main creditors and how much you owe them, use report templates for Xero & QuickBooks by Coupler.io. This makes it easier to prioritize payments to vendors.
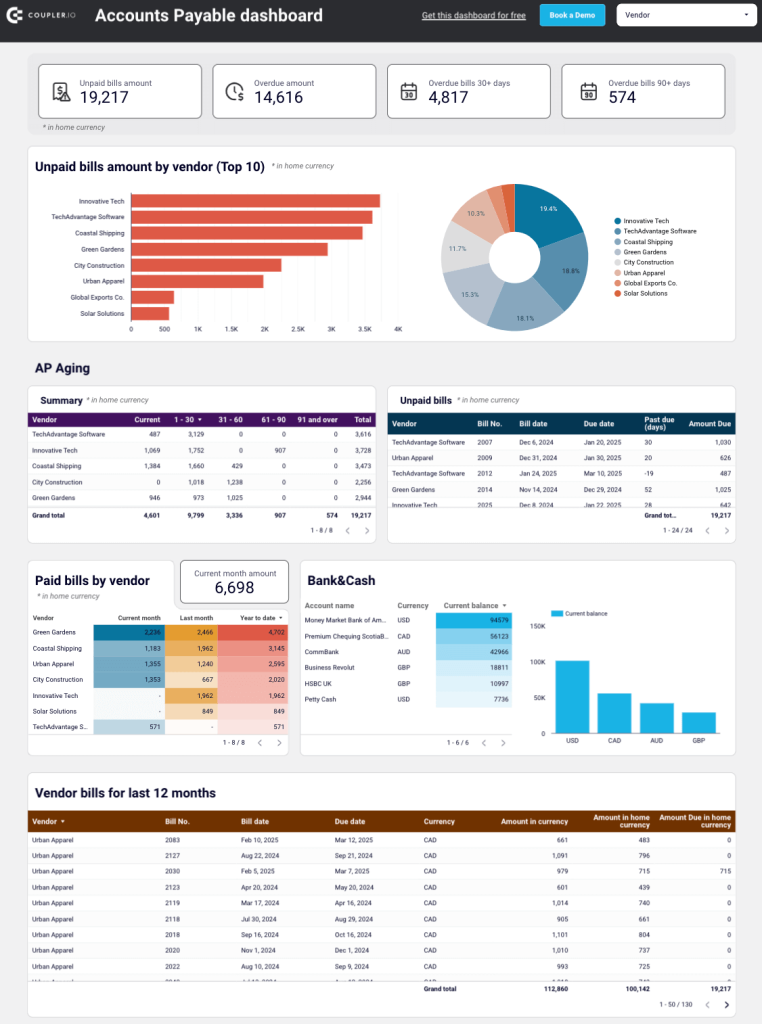
The dashboard is available for QuickBooks and Xero in Looker Studio and Google Sheets. To get started, click the template’s Readme tab and follow the straightforward setup guide.
3. Tax compliance
To fulfill tax obligations, avoid penalties, and maintain a good legal standing, ensure that you have a documented tax compliance SOP. This helps track deadlines, maintain proper financial records, and handle audits or inquiries.
Commonly, the procedure for tax compliance will comprise:
- Regulatory identification – define how the business identifies and stays updated with relevant local and national tax laws. This includes monitoring changes in tax regulations that affect the company’s operations.
- Tax recordkeeping – establish guidelines for maintaining accurate and organized records, including income documentation, deductible expenses, payroll taxes, and sales tax reports. Specify storage methods, retention periods, and access control.
- Filing and payment schedule – Outline the deadlines for submitting various tax returns and remitting payments. Assign responsibilities for preparing, reviewing, and filing tax documents. Establish procedures for scheduling internal reviews prior to submission.
- Compliance checks and reviews – decide how and when to conduct periodic internal audits, self-assessments, or reviews with external tax professionals. Indicate steps to identify noncompliance risks and implement corrective measures.
- Audit and dispute handling – provide a process for documenting all tax-related decisions and actions. Lay out protocols for responding to audits, managing inquiries from tax authorities, and resolving disputes through appropriate channels.
4. Budgeting and forecasting
In addition to day-to-day transactions, you must create, monitor, and adjust budgets in coordination with operational goals, anticipate future performance, and stay financially agile.
To support this, an SOP for budgeting and financial forecasting is needed. It should cover:
- Budget review schedule – define the timing and scope of monthly and quarterly budget reviews. Specify who participates in the reviews, what data to analyze, and how to document and communicate findings.
- Variance analysis – establish a consistent method for analyzing differences between budgeted and actual figures. Include steps to identify root causes, report variances, and recommend corrective actions.
- Team collaboration – outline how finance staff coordinate with relevant employees to gather input, validate assumptions, and refine forecast accuracy. Indicate the format, timing, and approval steps for any forecast updates.
To help predict your expenditures, use report templates such as the advertising budget forecast dashboard by Coupler.io. It allows you to project chosen metrics, such as amount spent, impressions, or clicks, for a specific period based on historical data.
Advertising budget forecast dashboard
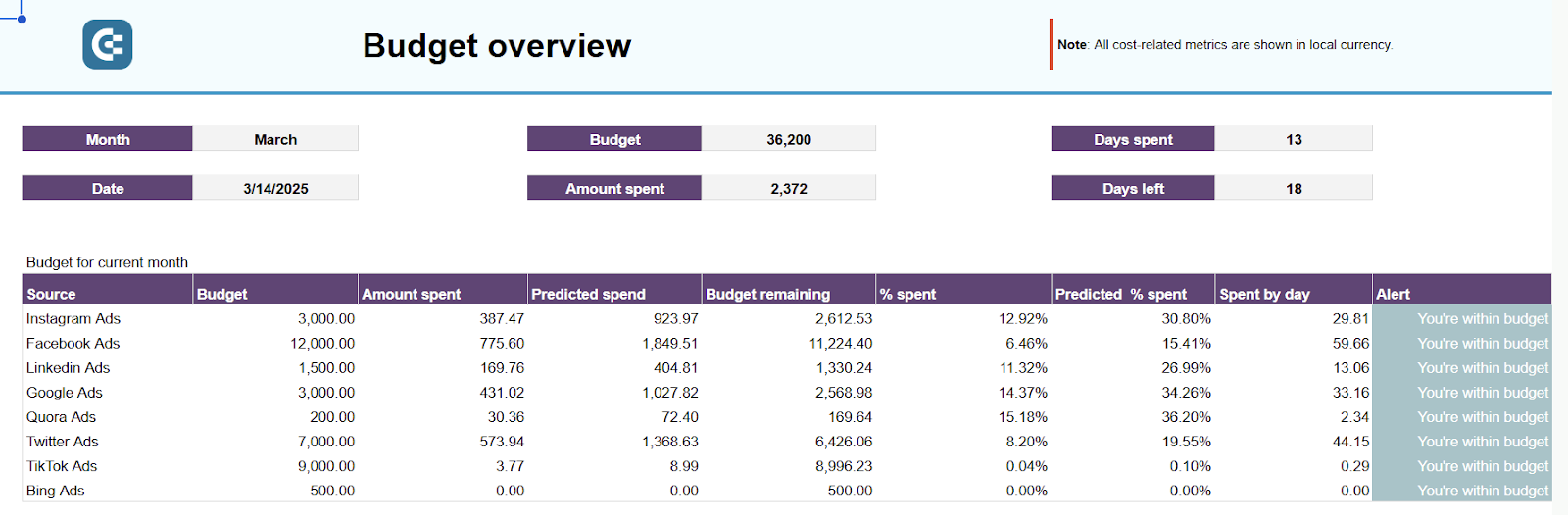 Preview dashboard
Preview dashboard
Advertising budget forecast dashboard
Preview dashboardThe dashboard aggregates data from Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, Google, Microsoft, TikTok, X, and Quora Ads. To set it up in Google Sheets, refer to the Readme instructions provided in the template.
5. Financial reporting and audit
To maintain transparency, meet regulatory obligations, and ensure informed decision-making, define an SOP for financial reporting and audit.
These are the key items that should be specified:
- Closing procedures – define month-end and quarter-end closing steps, including timelines, responsibilities, and checklists to capture and reconcile all financial activity.
- Financial statement creation – outline the process for compiling balance sheets, profit and loss reports, and cash flow statements with clearly defined roles and review protocols.
- Account reconciliation and documentation – establish how accounts should be reconciled and documented. Add guidelines for maintaining audit trails, supporting records, and exception reporting.
- Audit preparation – provide a clear structure for preparing ahead of internal or external audits. Explain how to collect required documentation, assign audit liaisons, and respond to auditor requests.
- Record keeping and authorization – lay out the process for organizing, storing, and signing financial documents. Indicate retention periods and who is authorized to review or approve reports.
- Data collection for reporting – export financial data from your systems: spreadsheets, project management tools, CRMs, accounting software, or other sources. The basic method would be to collect and consolidate this information manually, spending a few hours per week.
On the other hand, you’d better leverage Coupler.io to automate financial and accounting reporting since it allows you to:
- Pull data from over 400 sources, including business apps, databases, e-commerce tools, etc., enabling financial consolidation across all your business systems.
- Extract records from accounting and billing software: Xero, QuickBooks, and Stripe.
- Combine information from multiple disparate systems into a single source of truth.
- Create custom reports through aggregation, sorting, filtering, calculations, and more.
- Consolidate all data in spreadsheets or BI tools and set up a scheduled refresh.
- Get immediate insights into your business finances with pre-built dashboard templates.
Check out what it looks like to set up an automated data flow in Coupler.io
This tool for automated financial data analytics eliminates manual data entry, reduces human error, and ensures your reports contain accurate, up-to-date information from all relevant systems.
Automate financial reporting for your small business with Coupler.io
Get started for free6. Bank reconciliation
For financial reporting precision and consistency between internal records and actual bank activity, develop a dedicated procedure for reconciliation. This allows you to verify that all transactions recorded in the company’s books align with those processed by the bank.
Key components of a bank reconciliation SOP include:
- Retrieving bank statements – define how and when bank statements should be collected, along with access procedures and designated responsibilities.
- Reconciliation process – provide step-by-step instructions for comparing internal account balances to bank records. Cover verification of deposits, withdrawals, and cleared checks for alignment.
- Discrepancy investigation – establish a process for identifying and resolving mismatches, such as duplicate entries, bank errors, or timing differences.
- Approval of reconciliations – outline who is responsible for reviewing and approving completed reconciliations. Plus, indicate any sign-off requirements.
- Documentation and record retention – specify how reconciliation reports should be documented, stored, and retained for audit and compliance purposes.
- Data collection – decide how you’ll consolidate data to reconcile your transactions. Imagine you’re a company using a CRM like Salesforce to track customer transactions and record deals. When customers make payments, bank statements are sent to your accounting system, e.g., Xero. During reconciliation, these bank statements must be matched with the corresponding deals to ensure accuracy.
To simplify the process, collect your data for bank reconciliation using Coupler.io. For more details on how to do this, refer to our guide on automating your finance function.
7. Internal control
To protect financial integrity, reduce the risk of fraud, and ensure accountability, you need to build an SOP for internal controls. This way, you’ll strengthen oversight and create structure in daily financial operations.
The procedure must account for the following controls:
- Segregation of duties – indicate who is responsible for authorizing transactions, recording entries, and handling assets to prevent conflicts of interest or fund misuse.
- Access control – set rules for accessing financial systems, files, and data. Specify user roles, permissions, and restrictions.
- Recurring task management – outline how to handle routine financial responsibilities such as monthly reports, payment scheduling, or regular data updates.
- Payment reminders – define the method for managing payment reminders. Identify tools used, timing, and responsibility for follow-up.
- Approval methodology and process flow – describe how approvals are initiated, the criteria applied, the required authority levels, and the progression of decisions through the organization.
Now that you know the key SOPs for small business financial management, let’s find a way to keep their operation simpler and powered by data.
Advanced cash flow optimization in financial management for small business
According to a U.S. Bank study, 82% of small business failures are due to poor cash flow management. Beyond basic tracking, effective cash flow optimization requires strategic planning, operational efficiency, and smart financing decisions. Let’s explore advanced techniques to keep your business financially healthy.
Working capital optimization techniques
To maximize your available cash, focus on reducing the cash conversion cycle through three key areas:
Accelerate receivables collection — implement systematic follow-up procedures for overdue accounts, offer early payment discounts (e.g., 2/10 Net 30), and consider requiring deposits for large orders.
Optimize inventory levels — use ABC analysis to prioritize high-value items, implement Just-In-Time (JIT) ordering for non-critical supplies, and regularly review slow-moving stock for liquidation opportunities.
Extend payables strategically — negotiate Net 45 or Net 60 terms with suppliers while maintaining good relationships, and take advantage of early payment discounts only when cash flow allows.
Monitor these key performance indicators to track your progress:
- Current Ratio (current assets ÷ current liabilities) — aim for 1.2-2.0
- Quick Ratio (liquid assets ÷ current liabilities) — target 1.0 or higher
- Working Capital Turnover (revenue ÷ average working capital) — higher is better
Invoice financing and factoring strategies
When cash flow gaps appear, invoice financing offers immediate liquidity without taking on traditional debt:
Invoice financing allows you to borrow against outstanding invoices, typically advancing 70-90% of the invoice value. This works well for temporary cash needs while you maintain customer relationships.
Invoice factoring involves selling your invoices to a third party at a discount (usually 2-5% fee). The factor then handles collections, which can be beneficial if you lack robust collection processes.
The global factoring market is projected to reach $8,188.67 billion by 2030, indicating growing adoption among small businesses seeking flexible financing solutions.
Consider invoice financing when you have creditworthy customers with payment terms of 30+ days and need immediate cash for operations, payroll, or growth opportunities.
Seasonal cash flow smoothing strategies
For businesses with seasonal fluctuations, proactive planning prevents cash shortages during slower periods:
Create rolling 13-week forecasts — update weekly to anticipate cash needs and identify potential shortfalls early.
Build strategic reserves — accumulate cash during peak seasons and establish a seasonal line of credit before you need it.
Adjust operational costs — use temporary staffing, flexible lease terms, and variable supplier arrangements to match expenses with revenue cycles.
Renegotiate terms proactively — discuss seasonal payment arrangements with key suppliers and landlords before cash becomes tight.
Cash conversion cycle improvement
The cash conversion cycle (CCC) measures how long it takes to convert inventory investments back into cash. Calculate it as:
CCC = Days Inventory Outstanding + Days Sales Outstanding – Days Payable Outstanding
To reduce your CCC:
- Reduce Days Sales Outstanding (DSO) by implementing automated invoicing, following up promptly on overdue accounts, and offering early payment incentives
- Lower Days Inventory Outstanding (DIO) through better demand forecasting, supplier partnerships, and inventory management systems
- Increase Days Payable Outstanding (DPO) by negotiating longer payment terms while maintaining supplier relationships
Track your CCC monthly and benchmark against industry standards to identify improvement opportunities.
Simplifying small business financial management with report templates
To manage your SOPs more efficiently, you need up-to-date insights into your financial data on a regular basis. For this, Coupler.io offers free dashboard templates that enable you to monitor profitability, liquidity, cash flow, analyze revenue trends, identify growth opportunities, and more. Each template provides financial data visualization and has a built-in Coupler.io connector to ensure the data is automatically loaded into the dashboard. Let’s take a look at some of these templates.
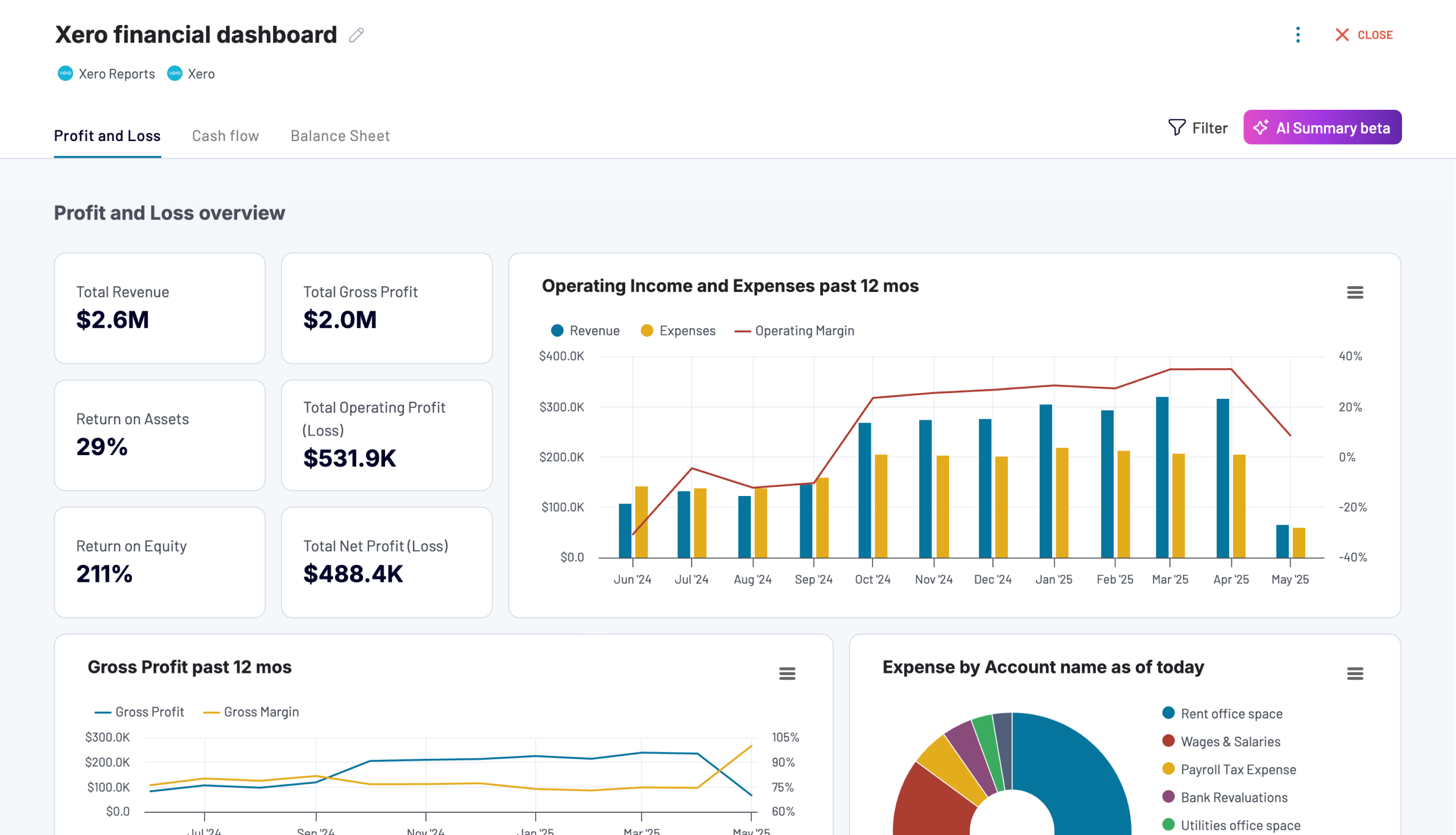
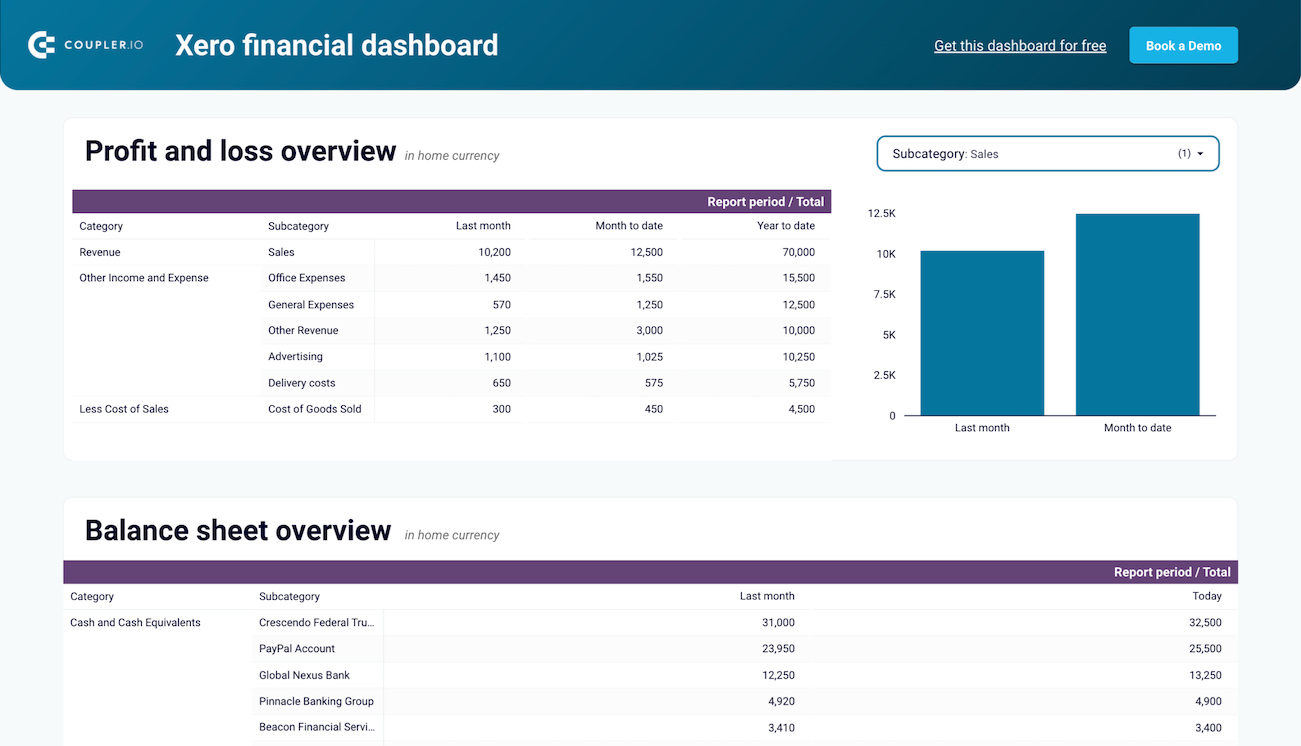
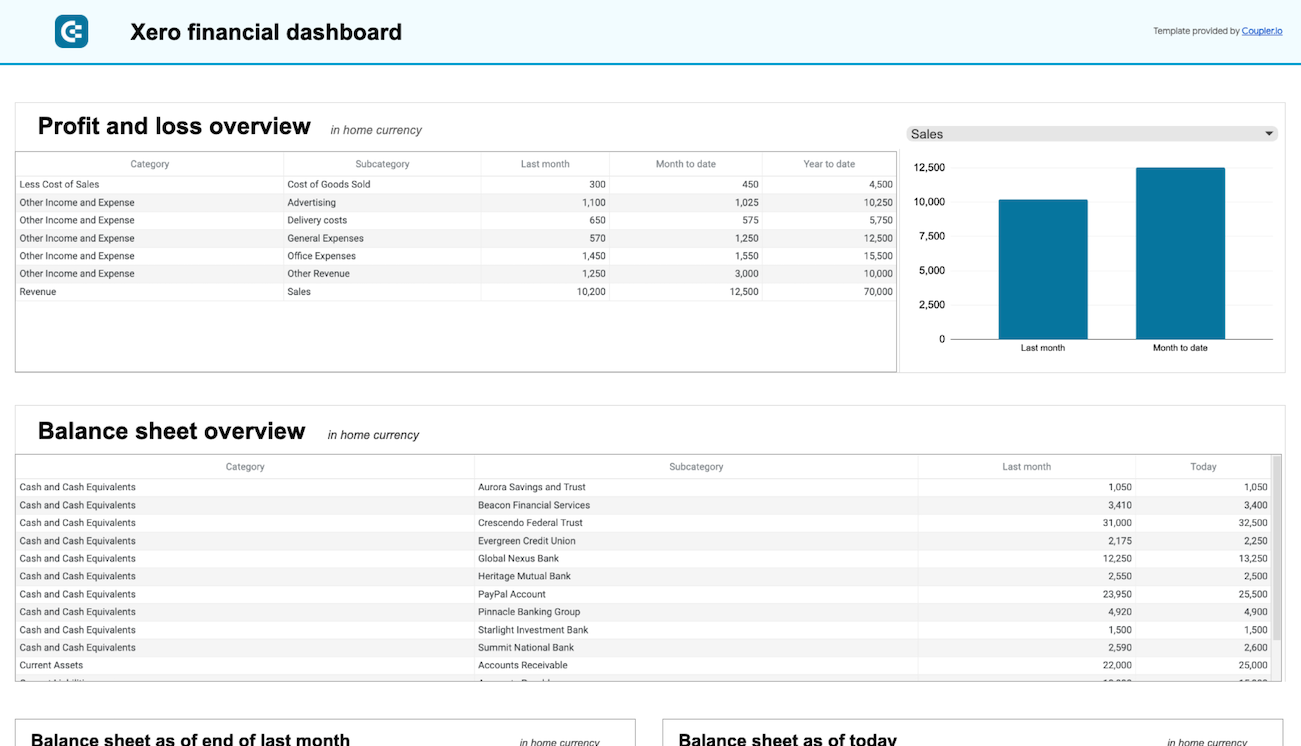
Financial dashboard for Xero/QuickBooks
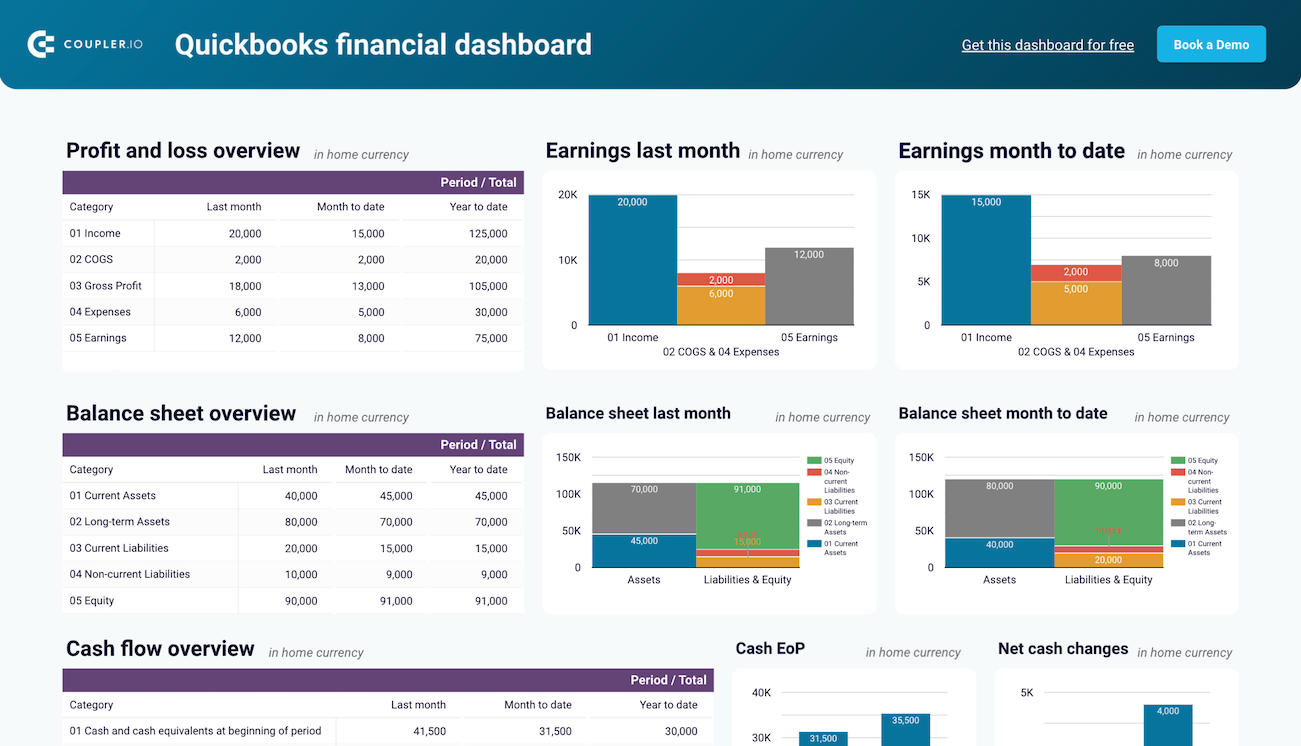
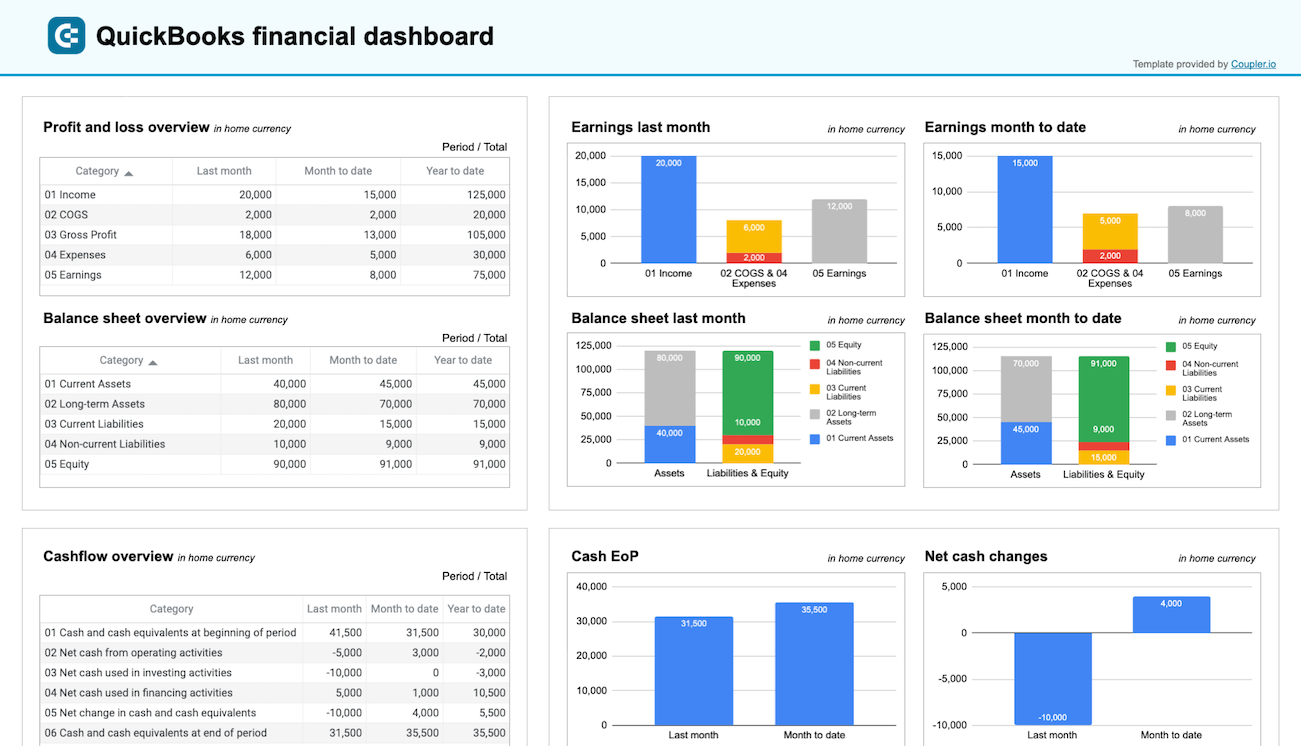
The financial dashboard by Coupler.io lets you track the company’s earnings, cash flow, and balance sheet changes. It’s perfect for an at-a-glance understanding of your business’s financial health without diving into detailed spreadsheets or reports.
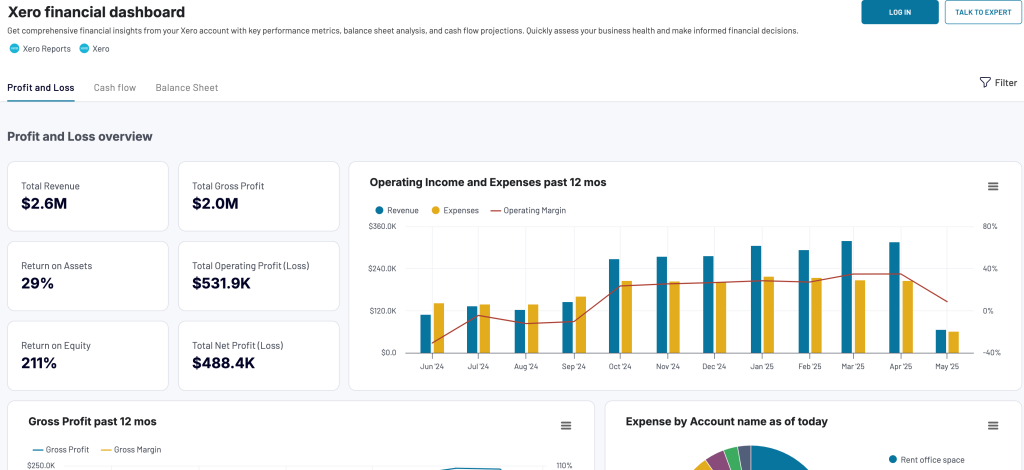
Leverage this dashboard to gain the following insights:
- Profit and loss overview: Get a summary of your revenue, business expenses, and net income for the last month, month to date, and year to date to monitor profitability and control your costs. Compare your earning trends to identify growth patterns or areas that need improvement.
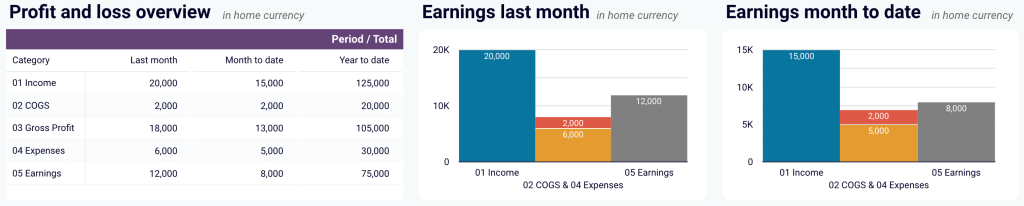
- Balance sheet overview: Take a snapshot of your assets, liabilities, and equity to understand your financial position, liquidity, and business health. Place your balance sheet assets alongside liabilities and equity for the last and current months.
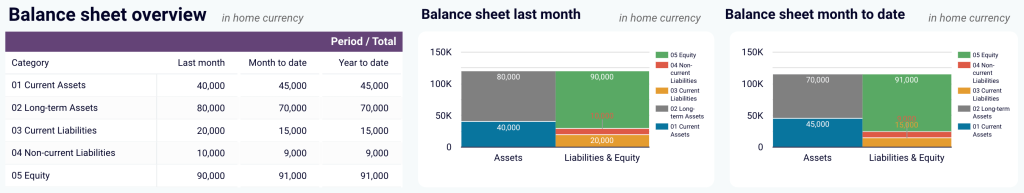
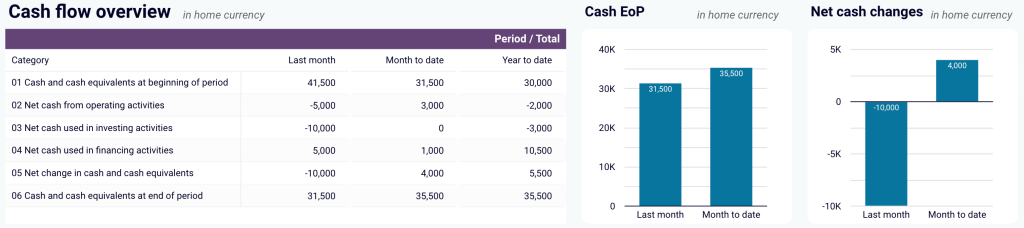
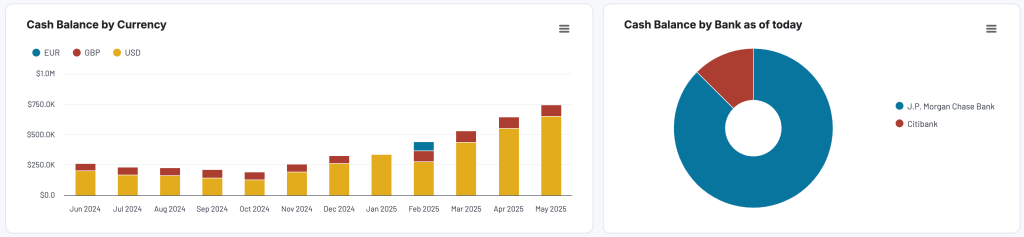
- Cash flow overview: Review net cash changes over the reporting period to track your position’s evolution and ensure effective liquidity management. Explore the cash position at the end of the period and the net changes to check your financial stability.
- Bank and cash accounts overview: Review your available funds and list the balances for all linked bank and cash accounts to verify that all are reconciled. You can also view balances by currency to simplify the monitoring of foreign accounts.
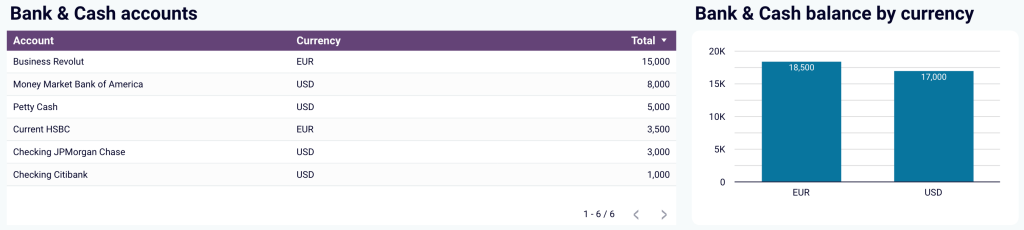
You can use the dashboard in Coupler.io, which offers the AI insights feature designed to help you quickly make sense of your data. Alternatively, set up a dashboard in Looker Studio or Google Sheets by following the instructions in the chosen template’s Readme tab.
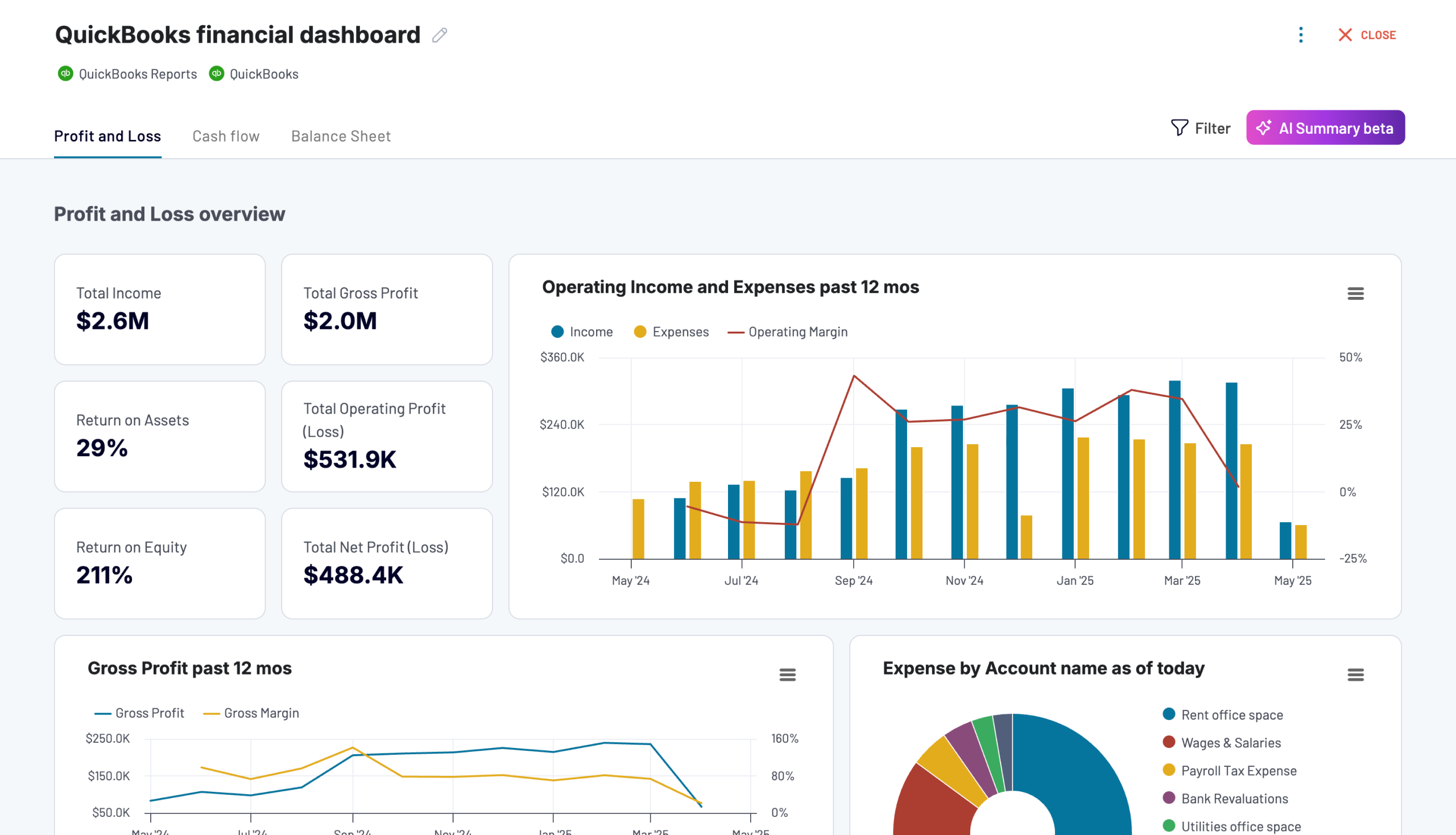
If you work with QuickBooks, Coupler.io also offers reporting solutions for this accounting software:
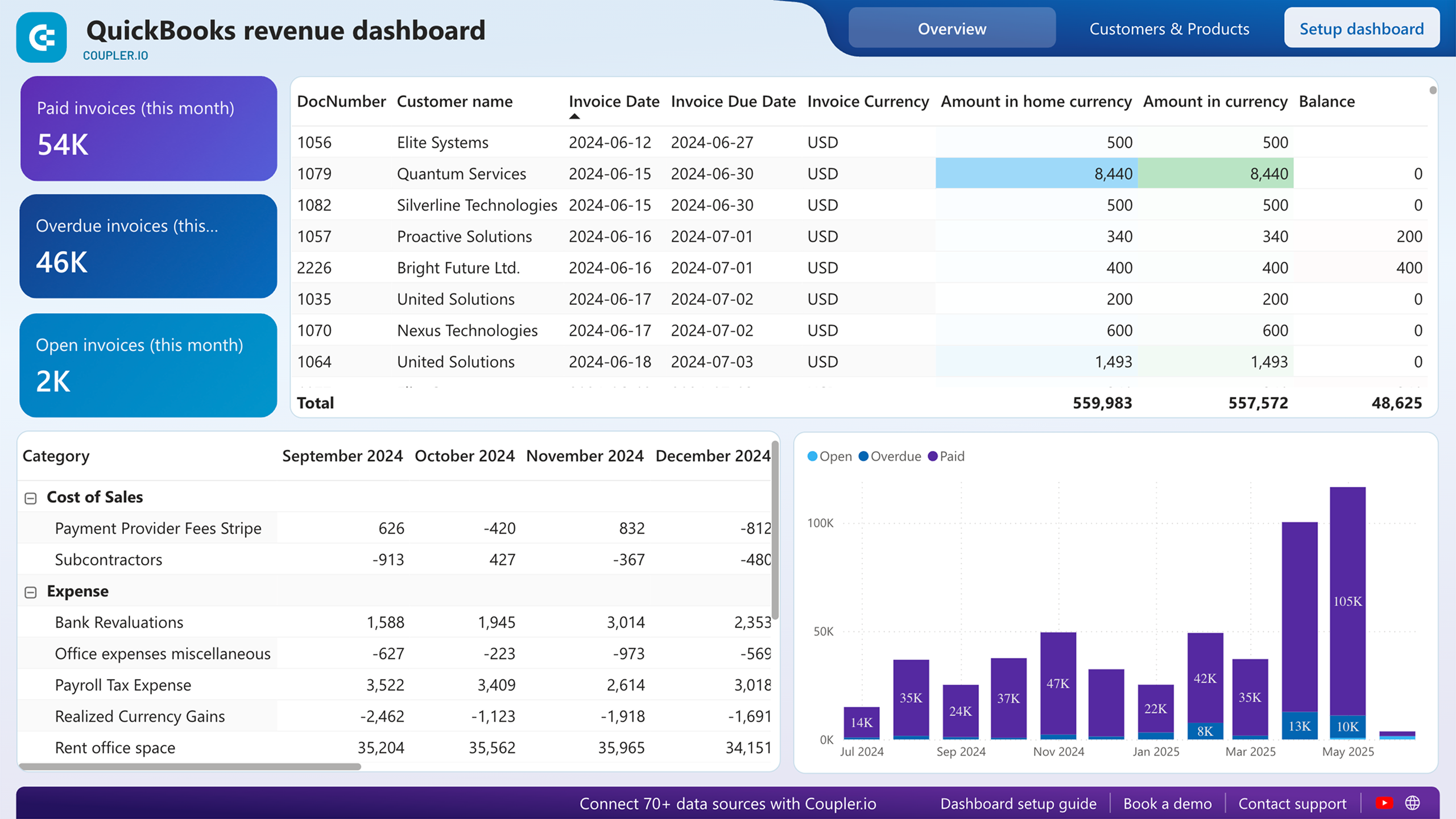
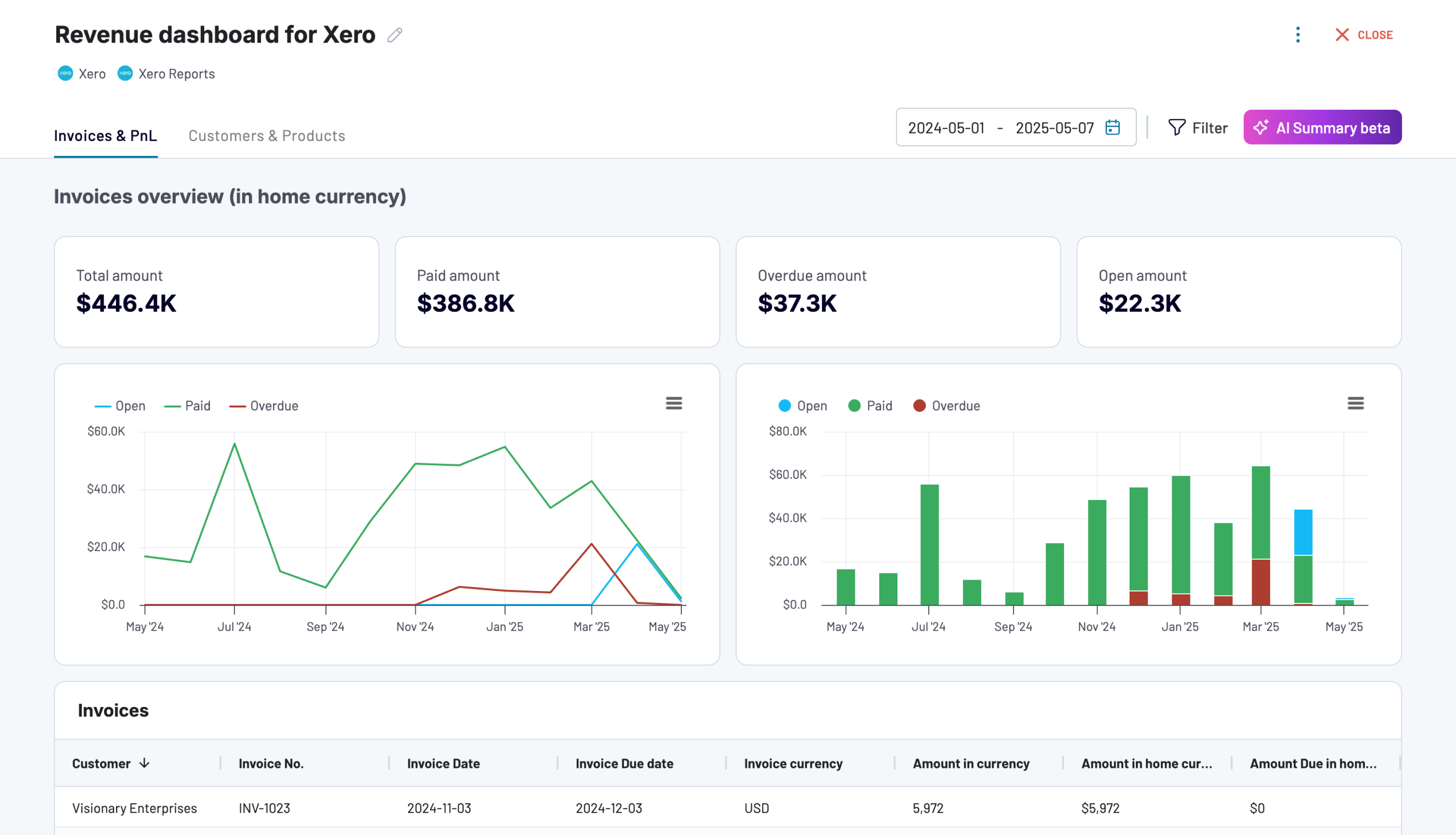
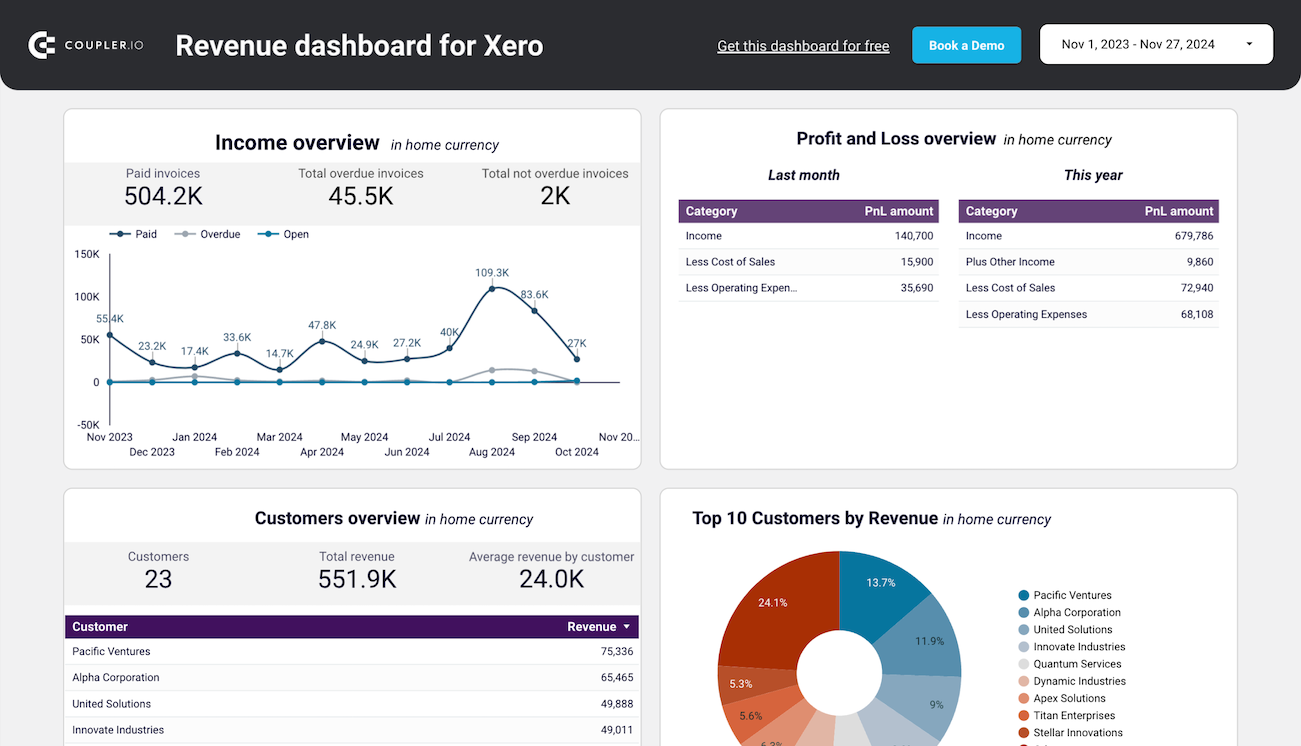
QuickBooks/Xero revenue dashboard
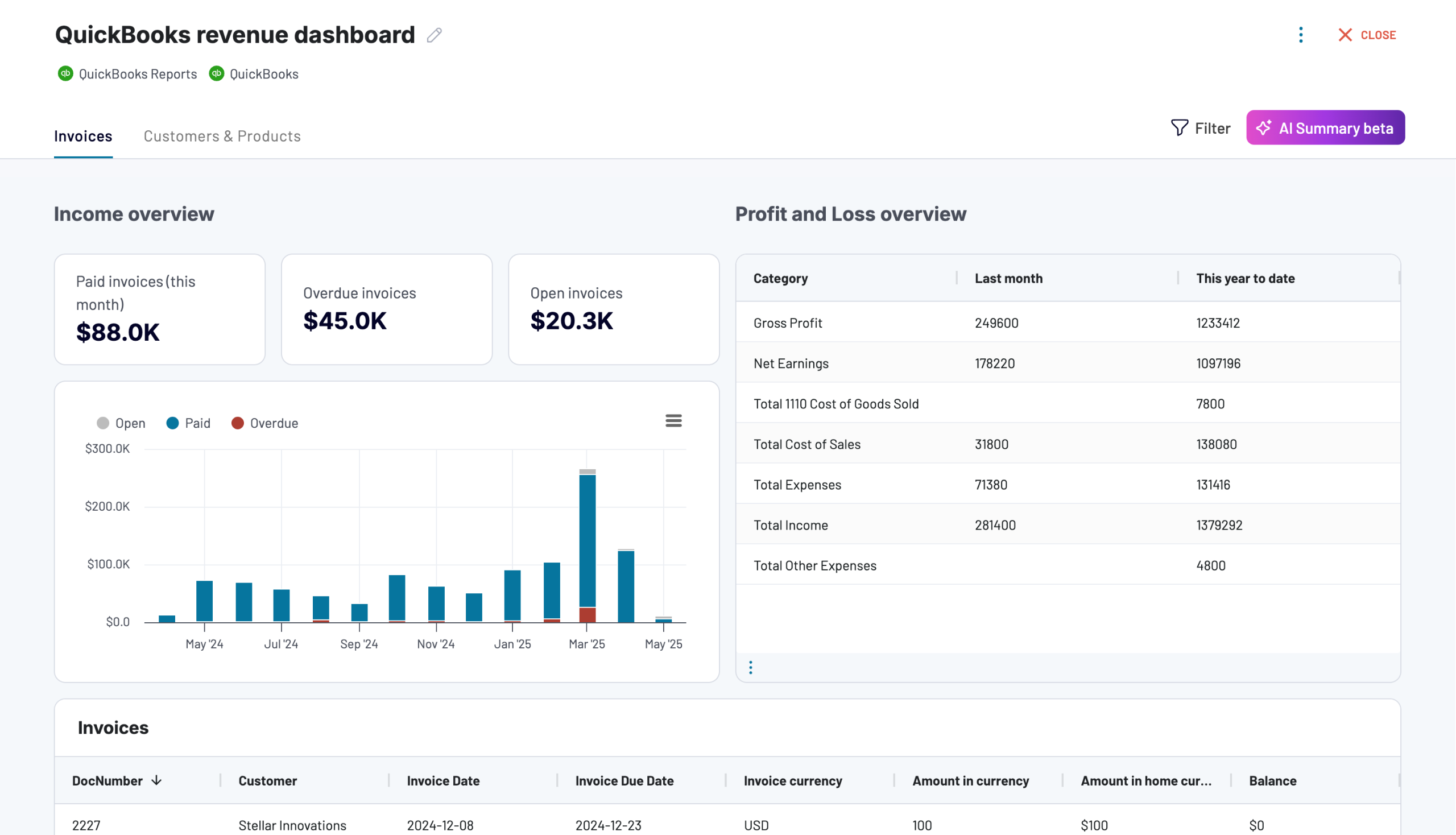
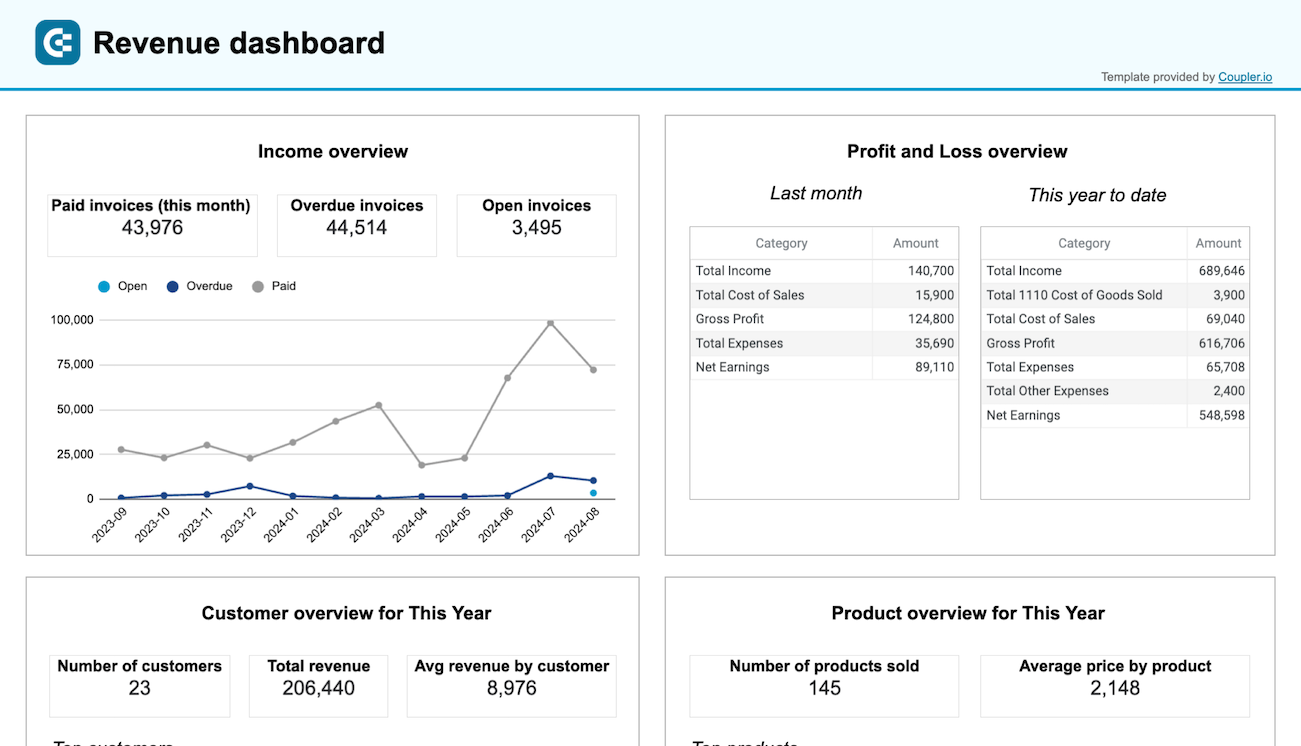
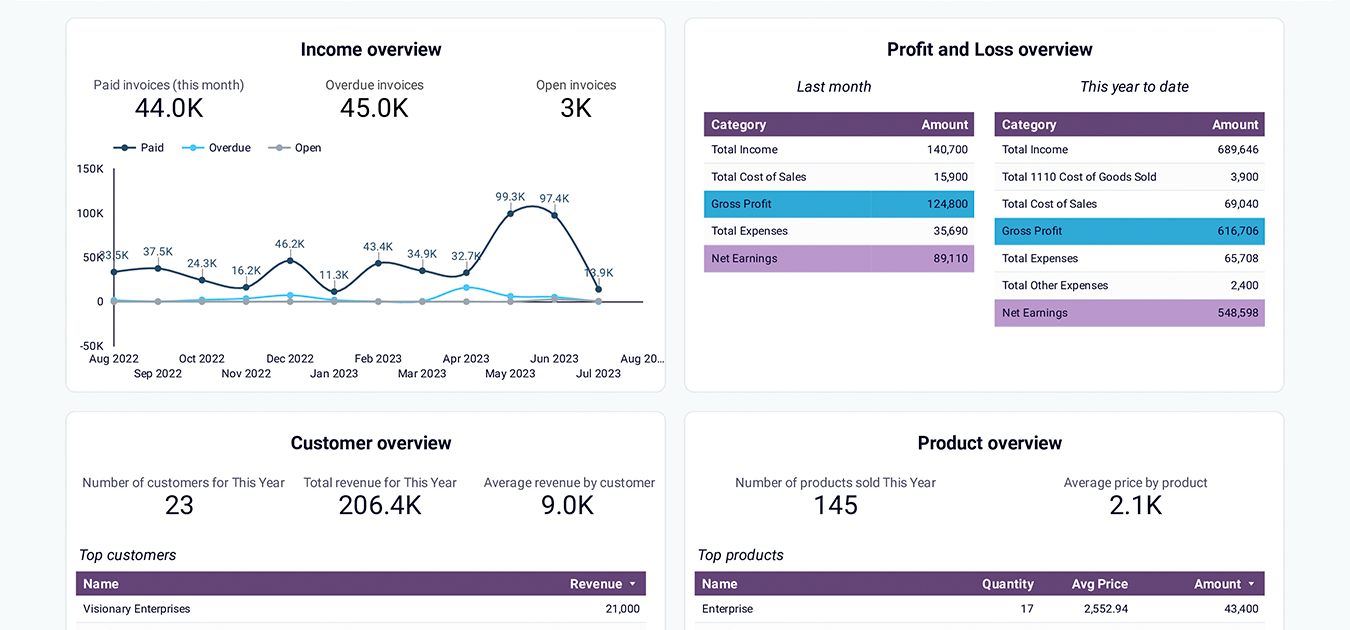
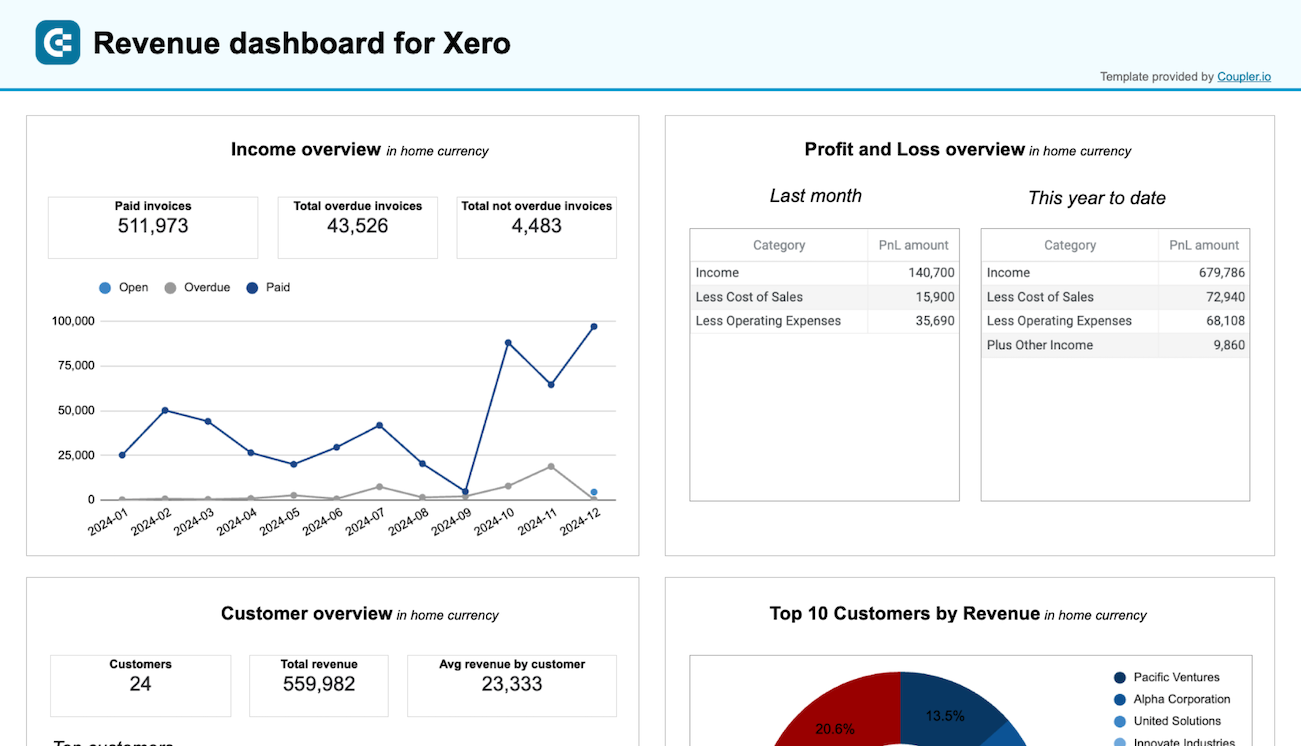
The revenue dashboard helps you monitor your income and expenses. It shows the revenue distribution by customers, aggregates key metrics, and displays your business’s top customers.
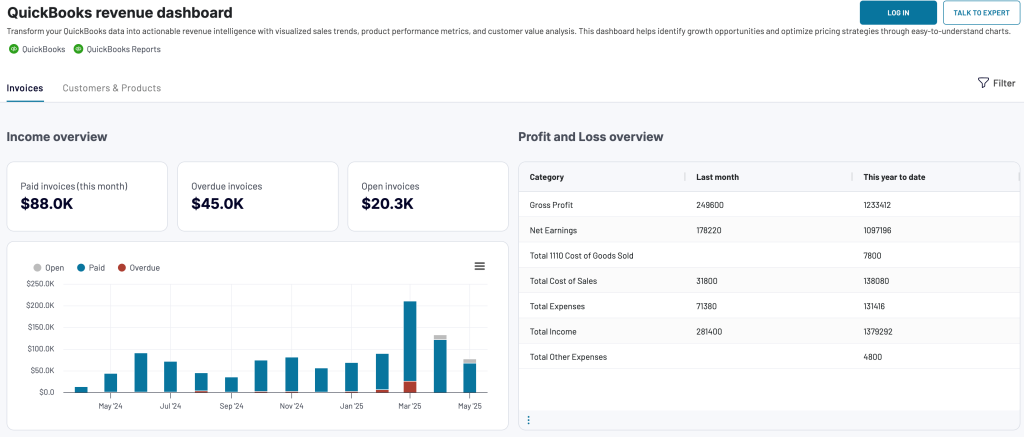
Below are the reports provided by the dashboard:
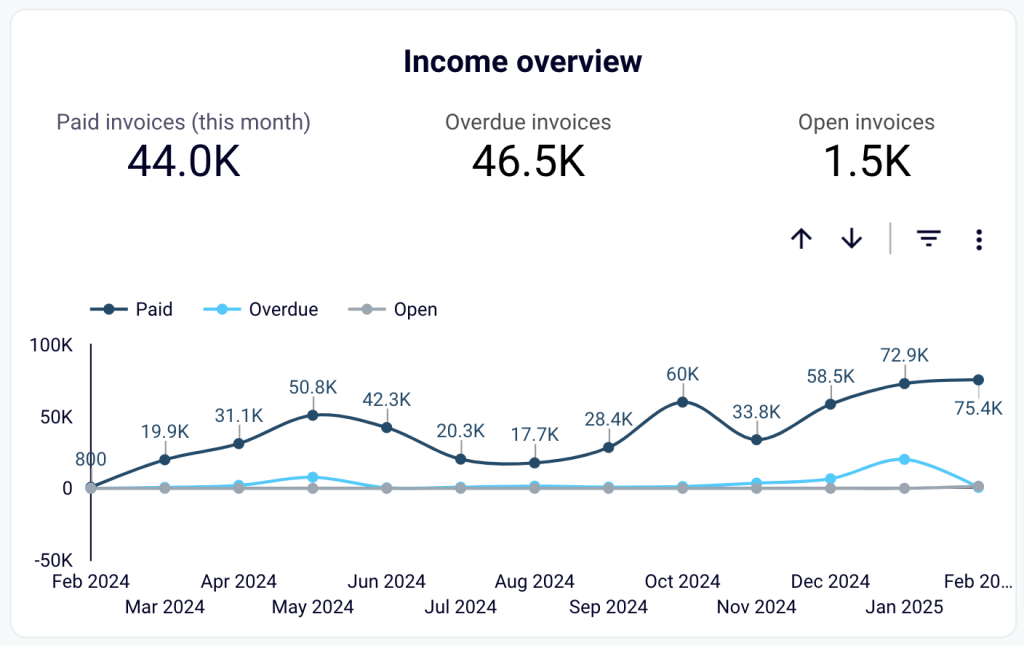
- Income overview: Track overall revenue trends for the last 12 months. Identify seasonal fluctuations, peak revenue periods, and any unexpected dips.
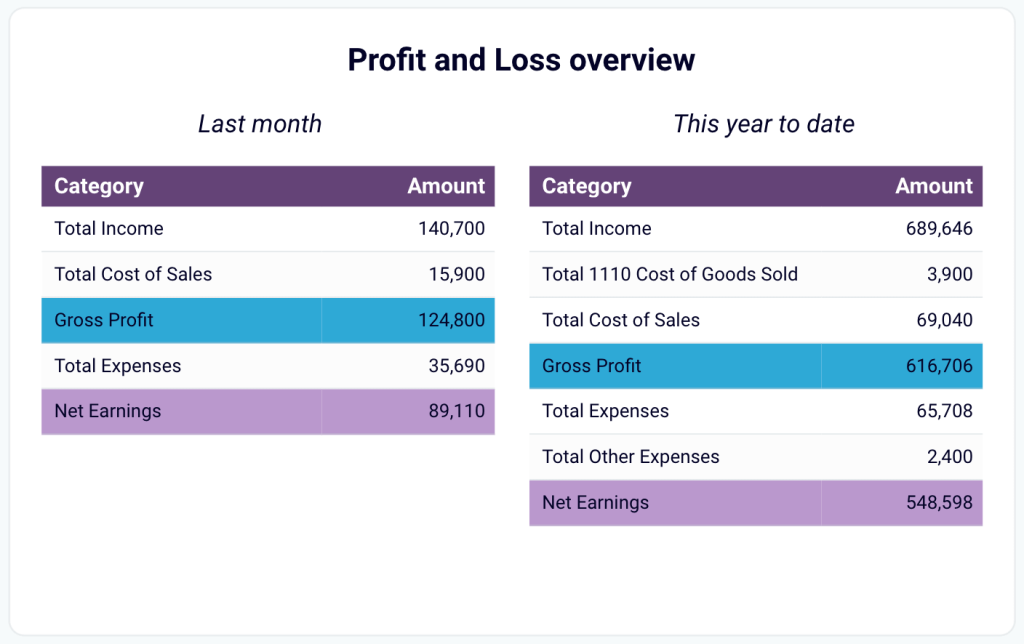
- Profit and loss overview: Compare revenue and expenses to gain insights into net income. Assess how effectively your business manages costs in relation to income to support your budgeting and financial planning.
- Customer overview: Identify your most valuable customers by revenue contribution to inform targeted marketing efforts and retention strategies. For example, you can provide loyalty incentives for high-value customers.
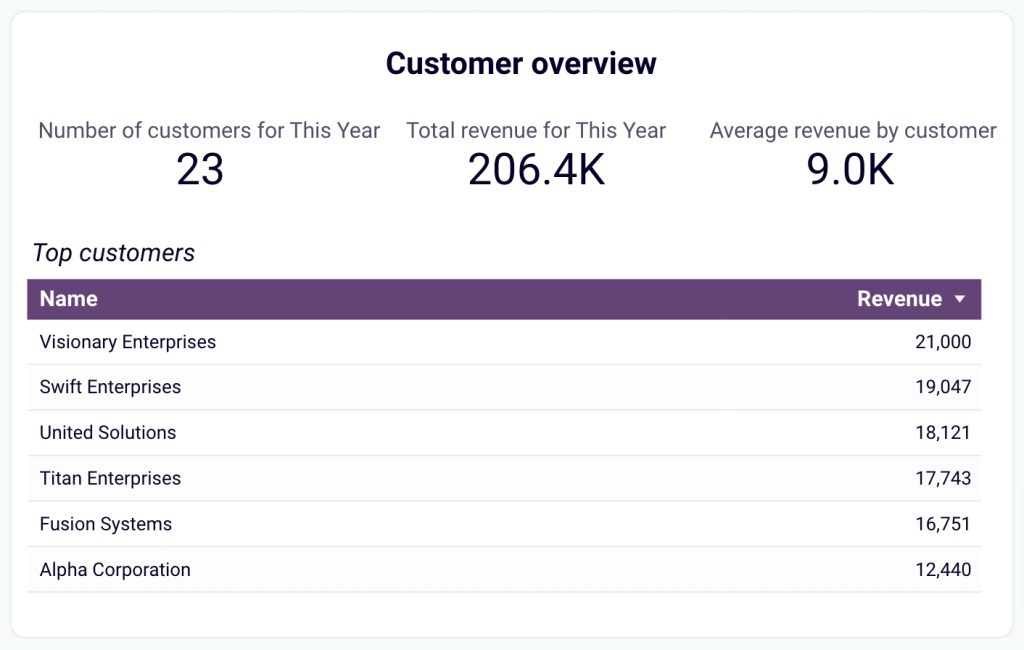
- Product overview: Figure out which products generate the most revenue. Based on information about high- or low-performing products, you can adjust your sales strategies.
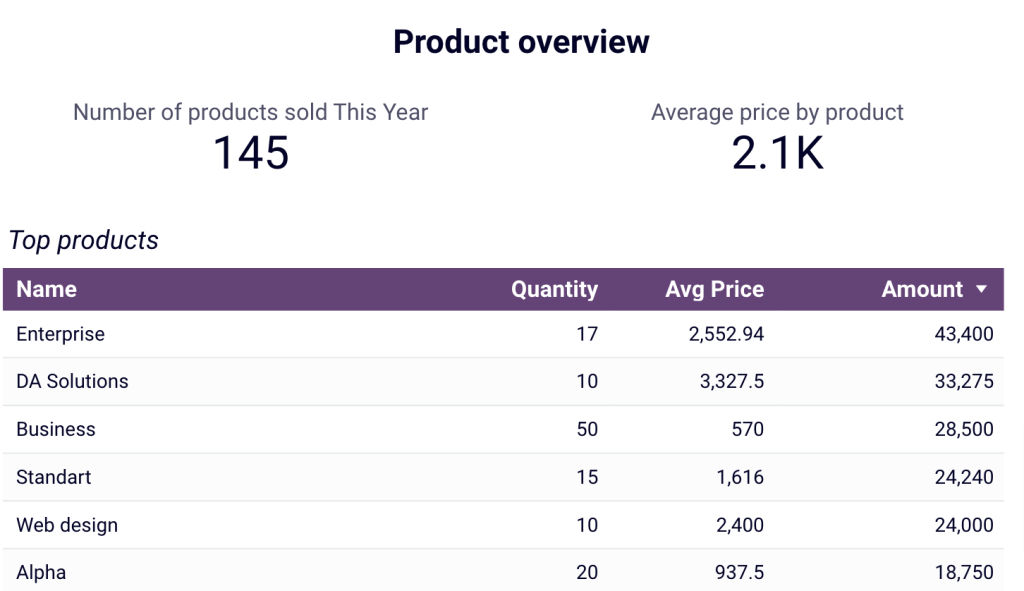
This dashboard can be used in Coupler.io UI (with AI insights) or, alternatively, in Looker Studio, Google Sheets, or Power BI for QuickBooks. To set up any of the alternative versions, navigate to the Readme tab inside the chosen template and follow the step-by-step instructions.
The Power BI version of the dashboard looks amazing! You can also learn more about Power BI financial reporting in our blog post.
If your accounting software is Xero, check out the revenue dashboard versions below:
Automating financial management for small business owners through technology
Manual financial processes are time-consuming and error-prone. Technology automation enhances accuracy, ensures compliance, and frees up time for strategic decision-making. Here’s how to leverage technology for more efficient small business financial management.
Comprehensive accounting software integration
Your accounting software should serve as the hub for all financial data. Popular options include QuickBooks, Xero, and Wave, each offering different strengths:
Integration capabilities — ensure your chosen platform connects seamlessly with your CRM (HubSpot, Salesforce), e-commerce platforms (Shopify, WooCommerce), and business intelligence tools (Looker Studio, Power BI).
Scalability considerations — select software that can grow with your business, handling increased transaction volumes, multiple currencies, and advanced reporting needs.
User accessibility — choose platforms that offer mobile apps and cloud access, enabling you to manage finances from anywhere.
Before committing to accounting software, test the integration capabilities with your existing tools. Poor integration leads to data silos and manual workarounds that defeat the purpose of automation.
Payment processing automation and optimization
Modern payment systems do more than process transactions — they automate your entire cash collection process:
- Automated invoicing and follow-up — platforms like Stripe, Square, and PayPal can automatically generate invoices, send payment reminders, and process recurring payments.
- Real-time reconciliation — automatic matching of payments to invoices eliminates manual data entry and reduces errors.
- Multi-channel payment acceptance — enable customers to pay via credit cards, ACH transfers, digital wallets, and mobile payments to accelerate collections.
- Advanced reporting — gain insights into payment patterns, customer behavior, and cash flow timing to improve forecasting accuracy.
Expense management and receipt digitization
Transform expense tracking from a monthly chore into a real-time process:
- Mobile receipt capture — apps like Expensify, Dext, and Zoho Expense allow employees to photograph receipts instantly, with AI automatically extracting key information.
- Automated categorization — machine learning algorithms categorize expenses according to your chart of accounts, reducing manual review time.
- Policy enforcement — set spending limits and approval workflows to prevent unauthorized expenses before they occur.
- Integration with accounting — seamlessly transfer approved expenses to your accounting system, maintaining accurate records without double entry.
Strategic API integrations
Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) connect your financial systems with other business tools, creating a unified data ecosystem:
- Banking integration — services like Plaid automatically import bank transactions into your accounting software, enabling real-time cash position monitoring.
- CRM connectivity — link customer data with financial records to track profitability by client, payment history, and credit limits.
- Project management integration — connect tools like Asana or Monday.com to track project costs and profitability in real-time.
For comprehensive data integration across multiple platforms, use Coupler.io. It lets you collect data from over 60 business applications into your preferred reporting tools. You can automate data flows and organize data on the go using filters, aggregations, and other features.
Cybersecurity essentials for financial data
As financial processes become more digital, security becomes paramount:
- Access controls — implement two-factor authentication on all financial applications and limit access based on job responsibilities.
- Data encryption — ensure all financial data is encrypted both in transit and at rest, meeting standards like PCI-DSS for payment information.
- Regular backups — maintain automated, encrypted backups of financial data with tested recovery procedures.
- Employee training — educate staff on phishing attempts, secure password practices, passkey usage, and proper handling of sensitive financial information.
- Compliance monitoring — stay current with regulations like SOC 2 for service providers and ensure your vendors meet appropriate security standards.
Financial management tips for small business
While SOPs play a leading role in financial management for small business owners, they aren’t enough on their own. To protect cash reserves, stay tax-compliant, and support sustainable growth, pay attention to the following key areas.
Control and manage debt
Most small businesses rely on some form of debt. To avoid being overwhelmed, take proactive steps to manage it:
- Step 1: Build an emergency fund – set aside cash regularly to cover unexpected expenses, such as equipment failure or delayed payments. This reduces reliance on high-interest borrowing.
- Step 2: Cut costs intelligently – trim non-essential expenses, such as excess office supplies or unnecessary cleaning services, without affecting core operations.
- Step 3: Boost revenue where you can – look for quick wins, like offering early payment discounts or subleasing unused office space. Ramp up proven marketing methods to generate sales.
- Step 4: Refinance or prioritize debts – lower your repayment burden by refinancing loans with better terms. Or pay off high-interest or personally guaranteed debts first.
- Step 5: Negotiate with suppliers – ask for discounts or more favourable terms, especially if you have a solid payment history. Partnering with others for bulk orders may also reduce costs.
- Step 6: Improve your credit score – maintain a low credit utilization rate. Ensure your credit report is accurate, and add any positive payment history manually if it’s missing.
- Step 7: Find funds to reduce debt – consider selling unused assets or attracting outside investment, although this may require relinquishing a portion of your business ownership.
Explore smart financing options
At some point, you’ll likely need funding, whether to address short-term cash shortages or fuel long-term success. So, choose your method strategically and stick to core principles.
Understand equity vs. debt financing
Equity financing involves raising capital by selling shares of ownership in your business. It improves cash flow and reduces financial risk, but dilutes control. On the other hand, debt financing preserves ownership but adds repayment pressure.
Know the pros and cons
While equity provides long-term support without immediate repayments, it can also create conflicts. In comparison, debt is predictable and tax-deductible, but it eats into cash and often requires collateral.
Choose the right type of financing
There are multiple types of financing to choose from, each suited to a specific context, and it is essential to understand them clearly.
| Type of financing | How it works | Best used for |
| Small business loan | A lump sum is borrowed from a bank (lender) and repaid over time with interest. | Ideal for creditworthy businesses with a solid relationship with their bank. |
| Crowdfunding | Funds are raised from a large number of individuals, usually via an online platform. | Helpful for unique products or causes that can gain public backing. |
| Invoice finance | You advance cash based on unpaid customer invoices, minus a fee. | Quick liquidity tool for businesses with outstanding invoices. |
| Business credit cards | This type of financing offers revolving credit with a limit. Interest applies if payment is not made in full monthly. | Applied carefully and sparingly to bridge short-term needs. |
| Grants | Governments or institutions provide funds without requiring repayment. | Non-repayable and highly competitive, suitable for innovation or socially beneficial businesses. |
| Venture capital | Investors provide capital in exchange for equity and strategic influence. | Relevant to high-growth startups willing to share ownership and decision-making. |
Improve your cash flow management
Poor cash flow is one of the most common reasons small entrepreneurs fail. To maintain liquidity and avoid running out of money, implement the following financial management tips for small business.
Set sensible payment terms
If offering credit to customers, balance attractiveness with sustainability. Consider shorter terms or incentives for early payment, and take action to discourage late payments, such as penalties or “due on receipt” clauses.
Vet clients before extending credit
To reduce default risk, conduct credit checks on new clients using tools such as Experian or Creditsafe. Avoid customers with poor credit or a history of financial difficulties.
Formalize payment terms
Even if payment terms are discussed verbally, follow up with a written agreement outlining all conditions. Include delivery terms and consequences of non-payment.
Build personal payment relationships
For timely payments, establish direct contact with those handling invoices. Confirm that all billing details are correct and proactively ask about potential delays.
Optimize cash flow management through automation
Well-informed cash flow decisions are not possible without fresh data insights. To make this happen, automate reporting with Coupler.io. You can build custom reports from your financial data and schedule them or set up self-updating dashboards using free templates.
Try Coupler.io for free and discover how it enhances financial management for small business.
Automate financial reporting for your small business with Coupler.io
Get started for freeRisk management and contingency planning
Unexpected financial shocks can devastate unprepared small businesses. From economic downturns to supply chain disruptions, having robust risk management and contingency plans protects your business when challenges arise.
Strategic emergency fund sizing
An emergency fund provides crucial breathing room during unexpected challenges. The optimal size depends on your business characteristics:
- Standard recommendation — maintain 3-6 months of fixed expenses in readily accessible accounts.
- Risk-adjusted sizing — seasonal businesses, those with volatile revenue, or companies in unstable industries should target 6-12 months of expenses.
- Revenue-based approach — some experts recommend 10-15% of annual revenue as an alternative metric, particularly for high-margin service businesses.
Calculate your emergency fund needs by listing all fixed costs: rent, salaries, insurance, loan payments, and essential utilities. This represents your monthly “survival” amount.
Build your emergency fund gradually by setting aside 5-10% of monthly revenue. Treat it as a non-negotiable expense, like rent or payroll, to ensure consistent funding.
Comprehensive business interruption planning
A Business Continuity Plan (BCP) prepares your company to operate during disruptions and recover quickly afterward:
- Risk assessment — identify potential threats specific to your business: natural disasters, cyber attacks, key employee loss, supply chain failures, or economic downturns.
- Critical operations identification — determine which processes are essential for survival and which can be temporarily suspended.
- Remote operations protocols — establish procedures for employees to work from alternate locations, including technology requirements and communication systems.
- Supplier backup plans — maintain relationships with at least two suppliers for critical materials and services to avoid single points of failure.
- Communication strategy — develop templates for communicating with employees, customers, suppliers, and stakeholders during crises.
Consider business interruption insurance to cover lost income during forced closures, ensuring you can maintain operations while addressing the underlying problem.
Revenue and supplier diversification strategies
Over-dependence on single sources creates dangerous vulnerabilities:
- Customer concentration risk — if any single customer represents more than 20% of revenue, actively pursue diversification. Companies with over 50% revenue from one client face extreme risk.
- Geographic diversification — expand your customer base across different regions to reduce exposure to local economic downturns.
- Product/service diversification — develop complementary offerings that appeal to different customer segments or serve countercyclical markets.
- Supplier redundancy — maintain qualified backup vendors for critical materials, even if they’re slightly more expensive. The insurance value outweighs the cost premium.
- Financial institution relationships — establish relationships with multiple banks to ensure continued access to credit and services if one institution changes policies.
Early warning systems for financial distress
Proactive monitoring helps identify problems before they become crises:
Key performance indicators to track:
- Gross margin trends (declining margins signal pricing or cost issues)
- Current ratio below 1.2 (indicates potential liquidity problems)
- Days sales outstanding increasing (suggests collection difficulties)
- Accounts payable aging extending (may indicate cash flow stress)
Monthly financial health checks — create dashboards using tools like Coupler.io to monitor these KPIs automatically, with alerts when metrics fall outside acceptable ranges.
Cash flow forecasting — maintain rolling 13-week cash flow projections, updating weekly to spot potential shortfalls early.
Vendor payment tracking — monitor your payment patterns to suppliers as an early indicator of cash flow stress.
Crisis cash flow management techniques
When financial crisis hits, swift action preserves your business:
- Expense prioritization — immediately categorize all expenses as critical (payroll, rent, loan payments) or deferrable (marketing, equipment upgrades, discretionary spending).
- Creditor communication — contact key suppliers and lenders proactively to negotiate payment deferrals or restructuring before missing payments.
- Revenue acceleration — offer discounts for immediate payment, liquidate excess inventory, or temporarily pivot to higher-margin services.
- Emergency financing — activate pre-arranged credit lines, consider invoice factoring, or explore emergency loan programs.
- Cash preservation — implement strict spending controls, require approval for all non-essential purchases, and consider temporary salary reductions for owners and key employees.
The key to crisis management is acting quickly and maintaining open communication with all stakeholders. Transparency builds trust and increases willingness to provide flexibility during difficult periods.